Figure 6.
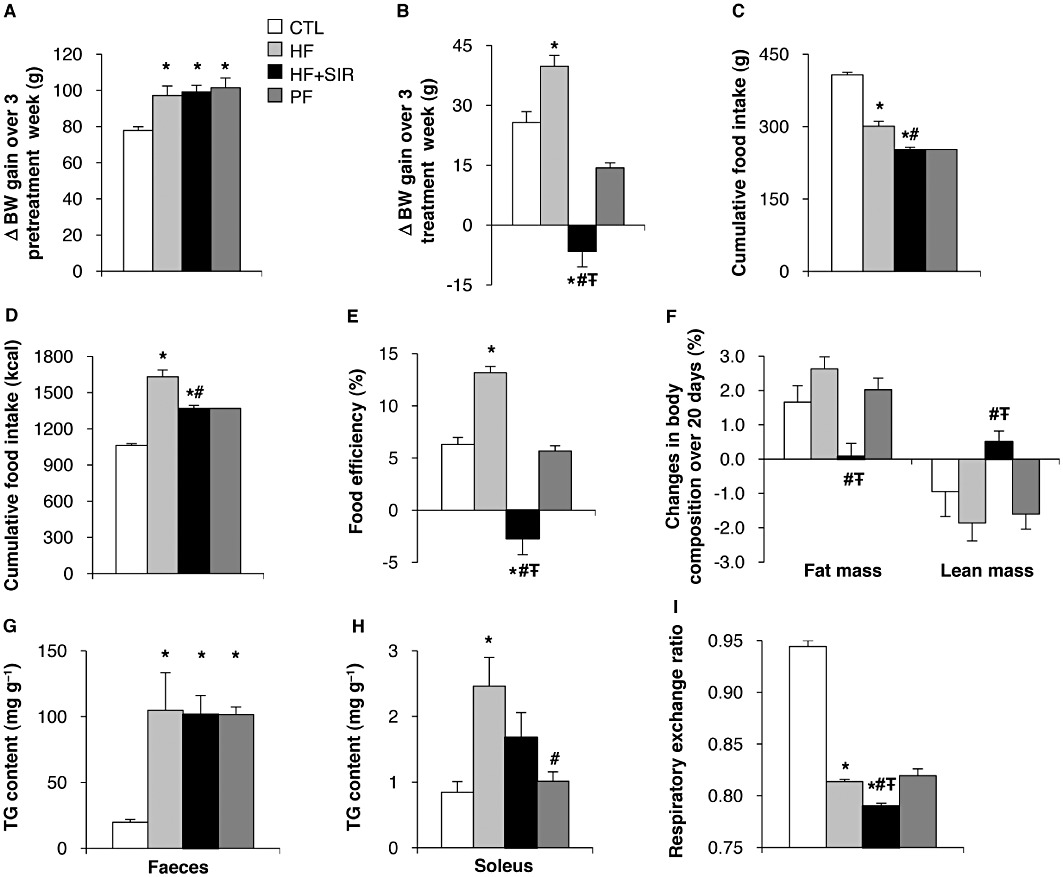
Effect of chronic Sirolimus administration on body weight (BW) gain and composition of Wistar rats fed a high fat (HF) diet. Wistar rats were fed a HF diet for 6 weeks. The last 3 weeks of the experiment, HF diet animals were chronically administered (for 3 weeks) either with vehicle (HF) or Sirolimus (HF + SIR). A third group of rats was pair-fed (PF) with Sirolimus-treated animals. An additional control group of rats (CTL) was fed a standard diet for 6 weeks. (A) Changes in BW of rats fed a standard or a HF diet during weeks 1 to 3 of the experiment. (B) Changes in BW of rats fed a standard or a HF diet with or without Sirolimus treatment during weeks 4 to 6 of the experiment. (C–D) Cumulative food intake over 3 weeks in g (C) and kcal (D). (E) Food efficiency [(BW gain/cumulative food intake) × 100] calculated over weeks 4 to 6 of the treatment period. (F) Changes in body composition determined by EchoMRI analysis over 20 days of treatment. (G) TG content in faeces, (H) TG content in soleus muscle and (I) respiratory exchange ratio (VCO2: VO2). Values are mean ± SEM of six rats per group. *P < 0.05 compared to standard diet fed controls. #P < 0.05 compared with HF diet-fed controls. ŦP < 0.05 compared with HF diet fed PF controls using anova followed by the post hoc Bonferroni test.
