Figure 6.
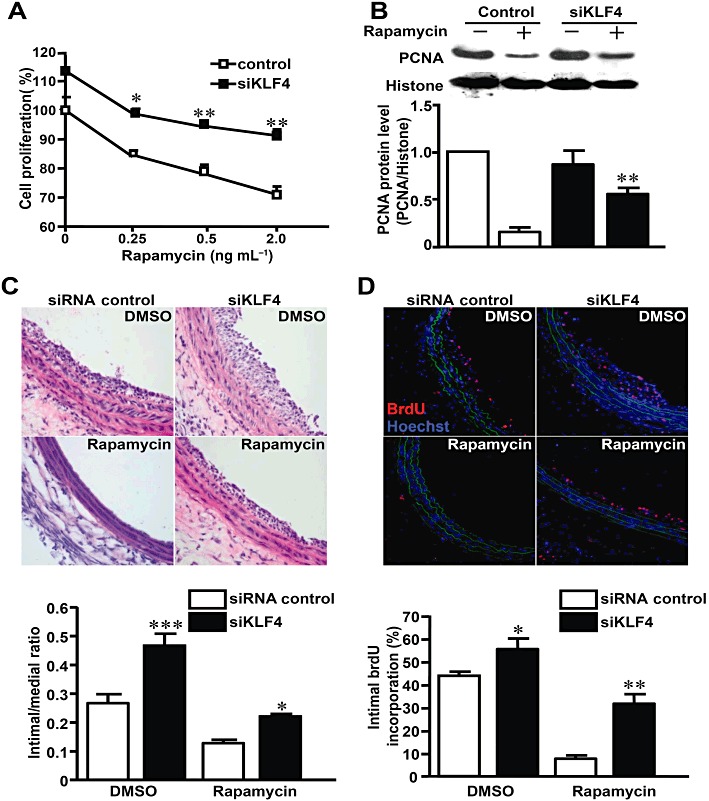
Knockdown of KLF4 suppressed the effect of rapamycin in vitro and in vivo. (A) After transfection with siRNAs, VSMCs were stimulated with 10% FBS and exposed to different concentrations of rapamycin or DMSO for 48 h. Cell numbers were counted and expressed as percentage of the DMSO-treated and control siRNA-transfected group. Comparison was made between siKLF4 and control siRNA groups at various concentrations of rapamycin. (B) After transfection with siRNAs, VSMCs were stimulated with 10% FBS in the presence or absence of rapamycin. Nuclear extracts were immunoblotted with antibodies against PCNA and histone 24 h later. (C) Rat carotid arteries were balloon-injured and treated with perivascular pluronic gel containing siKLF4 or control siRNA (15 µg per artery) and rapamycin (100 µg per artery) or DMSO. The injured arteries were harvested 7 days later and stained with haematoxylin–eosin. (D) BrdU incorporation was assessed 7 days later using anti-BrdU antibody (TRITC). Nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33258. The bar graph indicates the percentage of BrdU-positive cells in the neointima (n= 3 for each group). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, significantly different from siRNA control group.
