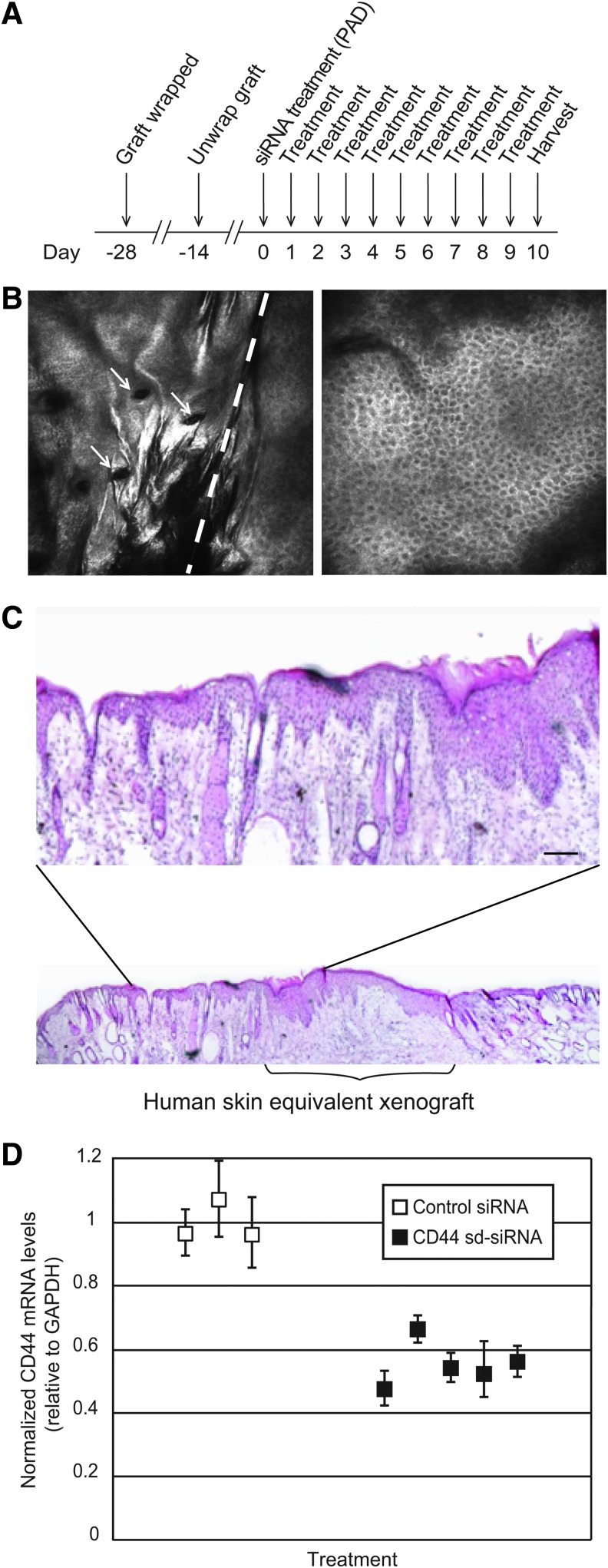
FIG. 3.
Inhibition of CD44 gene expression in human skin xenografts by CD44 sd-siRNA administered by microneedle arrays. (A) Schematic depicting experimental design. (B) In vivo images (see Materials and Methods) from full z-stacks (see Supplementary Videos S1 and S2 for the complete data set) of a human skin equivalent xenograft 4 weeks after grafting. Left: Mouse/human equivalent skin (left/right) border at a depth of 27 μm. Arrows indicate hair follicles present only in mouse skin. Right: Central image in human skin equivalent at 35-μm depth. Scale bar: 100 μm. (C) Hematoxylin–eosin (H&E) staining of a frozen section prepared from a human skin equivalent grafted on an immunocompromised mouse, 38 days postgrafting. Magnification shows mouse/human skin border. Scale bar: 50 μm. (D) CD44 siRNA-mediated inhibition of CD44 mRNA expression after siRNA administration by protrusion array devices (PADs). Human skin equivalents, grafted on immunocompromised mice, were treated with CD44 sd-siRNA or nonspecific control K6a_513a.12 sd-siRNA daily for 10 days by PAD administration. One day after the final treatment, the xenografts were harvested and subjected to RT-qPCR analysis to determine relative mRNA levels, using GAPDH as the reference gene. The standard errors represent qPCR triplicates of each sample.