Figure 8.
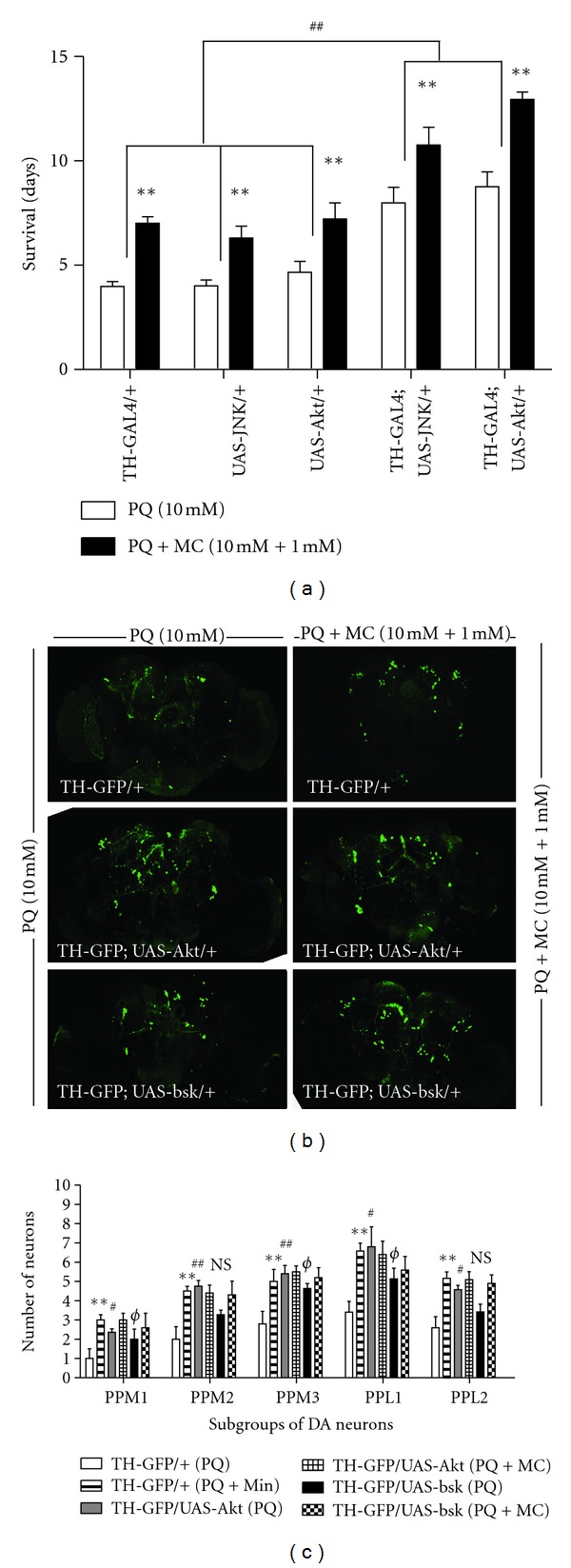
Overexpression of wild type BSK/JNK and Akt provides protection against PQ. (a) Adult males of genotypes TH-GAL4/+, UAS-bsk 1/+, UAS-Akt 1/+, TH-GAL4; UAS-bsk 1/+, and TH-GAL4; UAS-Akt 1/+ flies were fed, beginning at 48 hr after eclosion, 10 mM PQ or 10 mM PQ and 1 mM MC. The average survival duration for each group was determined. ** = P < 0.005 and represents significant differences between the PQ and PQ with MC groups. ## = P < 0.005, indicating a significant difference between control and JNK or Akt expressing flies fed only PQ. Error bars represent standard error of the mean. Each data point represents at least three independent replications of 50–60 flies each. (b) The effect of PQ (10 mM) and PQ + MC (10 mM + 1 mM) on brains of transgenic lines shown in the images. The overexpression of wild type Akt and Bsk/JNK in dopaminergic neurons provides protection to DA neurons against PQ, however; addition of MC in fails to provide additional protective to transgenic lines, TH-Gal4; UAS-eGFP/UAS-Akt WT and TH-GAL4; UAS-eGFP/UAS-bsk WT against PQ. (c) The average number of neurons per subset was determined 24 hr after the initiation of feeding in these transgenic lines. MC ingestion significantly improved the survival of DA neurons against PQ-induced loss of DA neurons in TH-Gal4; UAS-eGFP/+ brains.The overexpression of wild type Akt and JNK supports the survival of DA neurons against 10 mM PQ but addition of 1 mM MC failed to provide additional protection against PQ mediated DA neuron loss in these transgenic lines. ** = P < 0.005 and represent significant differences between PQ and PQ and MC-treated TH-Gal4; UAS-eGFP/+ brains. # represents significant differences between PQ-treated TH-Gal4; UAS-eGFP/+ and PQ-treated TH-Gal4; UAS-eGFP/UAS-Akt WT and Φ represent significant differences between PQ-treated TH-Gal4; UAS-eGFP/+ and PQ-treated TH-GAL4; UAS-eGFP/UAS-bsk WT brains, respectively. #/Φ = P < 0.05 while ## = P < 0.005. n = 8–12 brains for each transgenic lines. NS = not significant.
