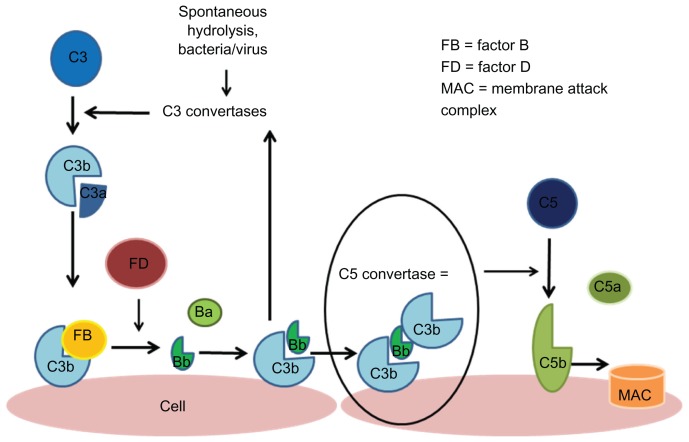
Figure 2.
Alternative complement pathway.
Notes: The alternative pathway is triggered by the hydrolysis of C3 which forms C3a and C3b. C3b becomes bound to the cell surface and is then able to interact with factor B, which is cleaved by factor D, creating the Bb fragment which binds to other surface-bound C3b molecules to form C3bBb; the C3 convertase of the alternative pathway triggers an amplification loop, with further hydrolysis of C3. Ultimately, there is further production of C3b which joins with C3 convertase to form C5 convertase which cleaves C5 to C5a and C5b, and this leads to formation of an membrane attack complex.108