Figure 1. Auto-immunity is preferentially observed in mixed chimeric mice.
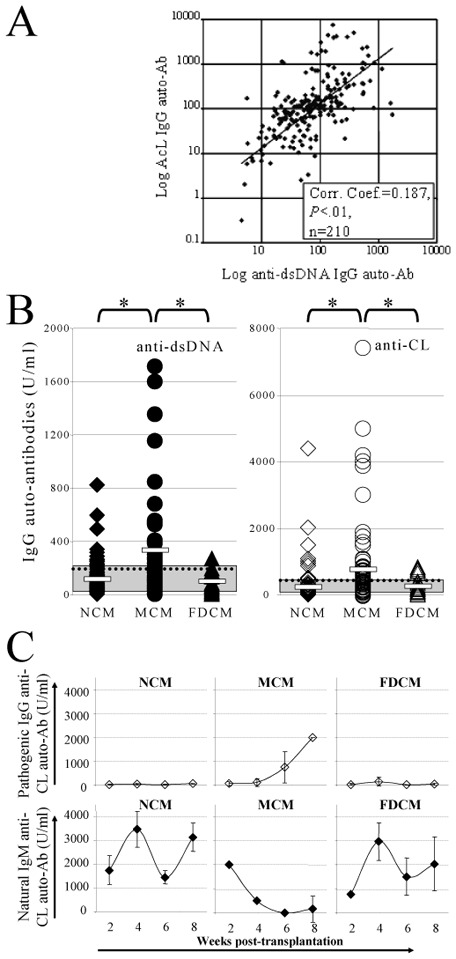
(A) A correlation between the levels of circulating anti-cardiolipin (AcL, x axis, Logarithmic representation) and anti-dsDNA (y axis, Logarithmic representation) IgG auto-Abs assessed by ELISA was found in recipient mice 9 weeks post-BMT. The solid line represents the calculated linear regression line of the observed data. Correlation coefficient =0.187, P<.01, n=210 recipient mice (Pearson Product Moment Correlation). (B) Circulating anti-dsDNA (black symbols - left hand side panel) and AcL (open symbols - right hand side panel) IgG auto-Abs were significantly higher 9 weeks post-BMT in mixed chimeric mice (MCM, circles) than in non- (NCM, diamonds) or full-donor chimeric mice (FDCM, triangles). White bars: mean for each group; doted line: mean of all groups; gray area: serum auto-Ab titers in 10 age-matched naive mice; *: P<.01 (Mann-Whitney Rank Sum Test). (C) Kinetics of both IgG (open diamonds) and IgM (black diamonds) AcL auto-Abs demonstrated a self-immunization in 4 out of 8 tested MCM, as attested by a simultaneous decrease of natural IgM auto-Abs and an increase of pathogenic IgG auto-Abs. In contrast, low levels of pathogenic IgG auto-Abs and normal levels of natural IgM auto-Abs (as compared to age-matched naive mice, range of AcL IgM auto-Ab titers: 2210.8–4358.3 U/ml) were observed in NCM (n=8) and FDCM (n=8). Error bars: SEM.
