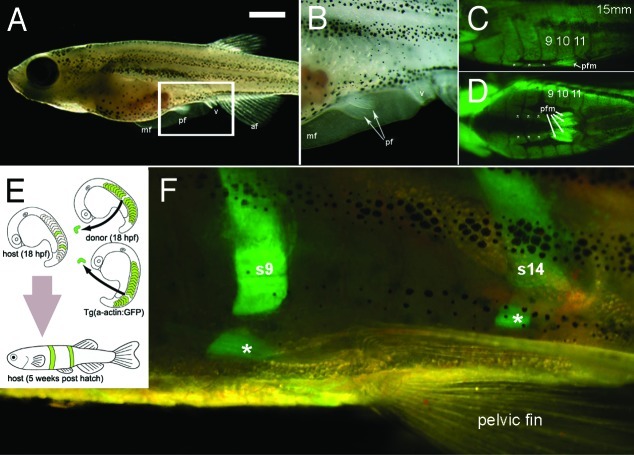
Figure 2. Pelvic fins, musculature and transplantation in zebrafish. (A) Lateral view of a 5 week old zebrafish. Scale bar= 1 mm. (B) Higher magnification view of area boxed in (A). (C and D) Lateral view (C) and ventral view (D), of green fluorescent protein (GFP) expression in muscle of the Tg(acta1:GFP)zf13 zebrafish. The pelvic fin muscles (pfm) and line of muscles ventral to and separate from each myotome can be seen (white asterisks). (E) Cartoon detailing method of double transplant of two GFP positive somites into wild type host. (F) Detail of pelvic fin region of GFP positive donor somite 9 and 14 in to wild type host zebrafish. The donor GFP somite does not form pelvic fin muscles in the host but does contribute to the muscles (white asterisks) ventral to and separate from the corresponding somite. Abbreviations mf, median fin; pf; pelvic fin, v; vent, af, anal fin, pfm pelvic fin muscle, s9, s14 somites 9 and 14.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.