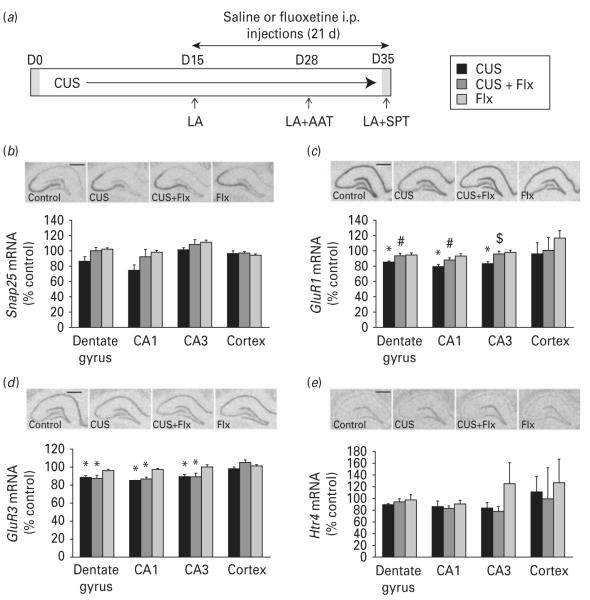
Fig. 4.
Effects of chronic unpredictable stress (CUS) and antidepressant treatment on expression of selected human target genes in the rat hippocampus. (a) Rats were exposed to CUS or control housing conditions ; saline (vehicle) or fluoxetine (Flx) were administered for the last 21 d of stress. CUS had no effect on the locomotor activity (LA), but evoked increased helpless behaviour in active avoidance test (AAT) and reduced sucrose intake in sucrose preference test (SPT) ; both of these behavioural effects of CUS were reversed by chronic Flx treatment (data not shown). Representative autoradiographs and quantitative analysis of (b) Snap25, (c) GluR1, (d) GluR3 and (e) Htr4 mRNA levels by in situ hybridization on coronal sections of dorsal rat hippocampus (scale bar, 1.0 mm). Results are expressed as mean±s.e.m. percent change over non-stressed control group (n=4or 5) ; * p<0.05 compared to the non-stressed control group, # p<0.05 compared to CUS group, $ p<0.07 compared to CUS group (two-way analysis of variance and Fisher’s PLSD post-hoc analysis).