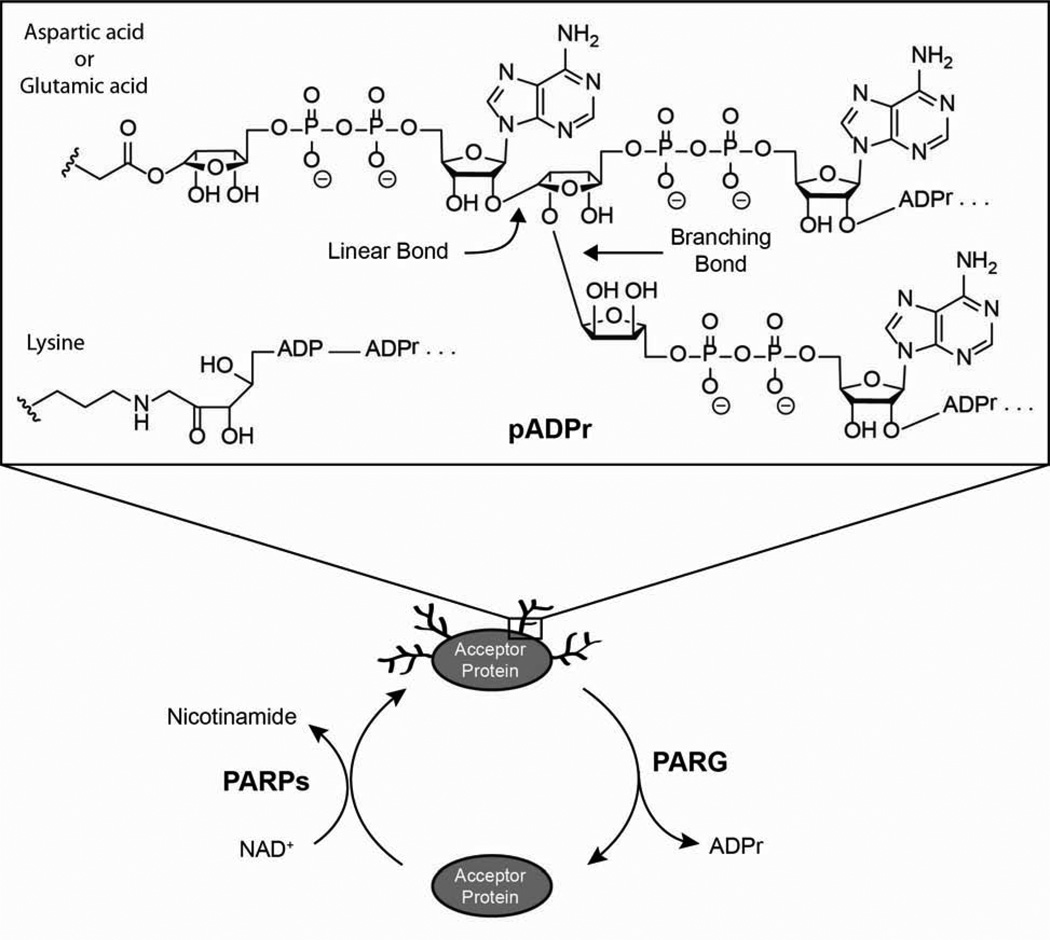
Figure 1.
The metabolism of poly(ADP-ribose) [pADPr]. PARPs [poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases] biosynthesize pADPr from NAD+ while PARG [poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase] degrades polymer to ADP-ribose [ADPr]. PADPr is covalently attached to aspartic acid, glutamic acid, or lysine residues of acceptor proteins and the ADPr units of the polymer are connected linearly or in a branched fashion.