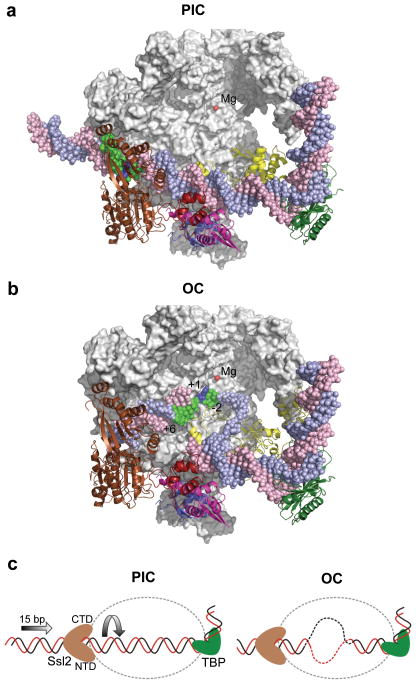
Figure 8.
Comparison of the PIC and open complex (OC) models suggests the role of Ssl2 in DNA strand opening. (a) The PIC model containing Pol II (grey), TBP (dark green), TFIIB (yellow), TFIIE (Tfa1 WH (blue), Tfa2 WH1 (red), and Tfa2 WH2 (pink)), Ssl2 (brown) and the active site Mg2+ (red). Rpb2 is removed to allow viewing into the Pol cleft. The blue template strand DNA is colored green from position −2 to +6 relative to the mammalian transcription start site (blue). (b) The OC model where double stranded DNA in the PIC was replaced with the DNA from the OC model 9. Compared to the PIC, 15 bases of upstream DNA is moved into the Pol II cleft and template strand DNA spanning positions −2 to +6 (green) relative to the transcription start site +1 (blue) is positioned close to the active center. (c) Diagram of Ssl2 function in OC formation. In the left panel, upstream promoter DNA is in a fixed position due to binding by TBP/TFIIB/Pol II. Ssl2 lies on downstream DNA at a fixed position due to interaction with TFIIE. Ssl2 feeds DNA into the cleft by a right handed threading mechanism, rotating and unwinding DNA.