Figure 1.
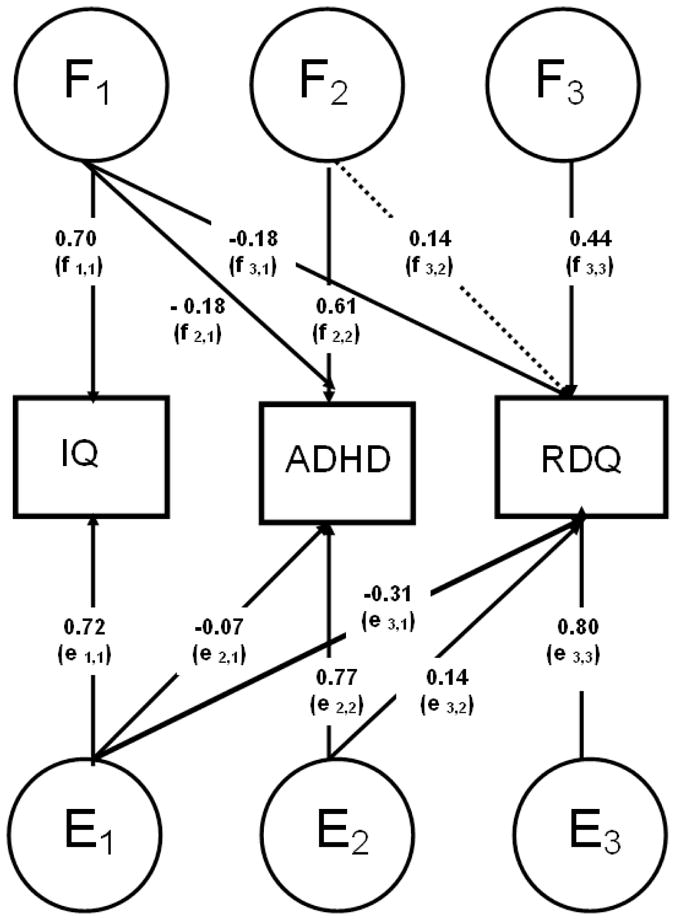
Parameters F1–F3 and parameters E1–E3 are estimates from Cholesky models estimating the familial and child-specific environmental factors across IQ, ADHD and Reading Difficulties Questionnaire (RDQ), respectively. Significant paths (p<0.05) are indicated as solid lines and non-significant paths (p≥0.05) are indicated as dotted lines.
Note: Parameters F1–F3 represent familial influences on and between the traits. f1,1 represents the sum of the familial influences underlying IQ. f2,1 represents the familial influences from IQ that are also shared with ADHD, while parameter f2,2 represents those familial influences that underlie ADHD, and are not shared with IQ. The sum of familial influences underlying ADHD is therefore the sum of f1,1 (those shared with IQ) and f2,2 (those not shared with IQ). The same inferences apply to RDQ, such that f3,1 represents familial influences underlying RDQ that are shared with ADHD (and to some extent ADHD), f3,2 represents familial influences shared between ADHD and RDQ only, and f3,3 represents familial influences specific to RDQ only. The sum of these three paths represents the sum of all familial influences underlying RDQ. The same inferences can be made for the E parameters, which represent child-specific environmental influences (and subsume any measurement error).
