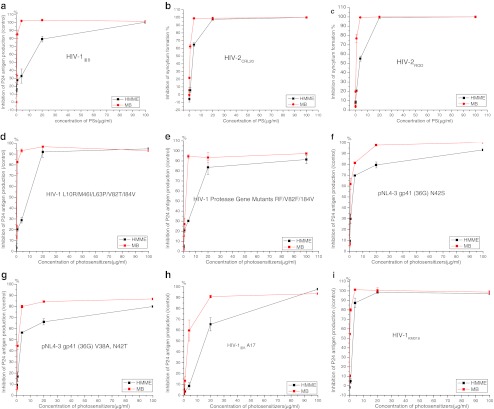
Fig. 2.
a–c Inactivation of HIV-1IIIB, HIV-2, resistant HIV-1 and HIV-1 clinical strains induced by PDT HIV-1IIIB (a), HIV-2CRL20 (b) and HIV-2ROD (c). The efficacy of PDT was expressed as the inhibition rate of syncytium formation. d, e Inactivation of protease inhibitor-resistant HIV-1 variants HIV-1 L10R/M46I/L63P/V82T/I84V (d) and HIV-1 protease gene mutants RF/V82F/184V (e). f, g Efficacy of PDT against the enfuvirtide-resistant HIV-1 variants pNL4-3 gp41 (36G) N42S (f) and pNL4-3 gp41 (36G) V38A, N42T (g). h, i Inactivation of the reverse transcriptase non-nucleoside inhibitor-resistant variant HIV-1IIIB A17 (h) and HIV-1KM018 (i). p24 antigen production was used as a measure of PDT-induced inactivation of HIV-1-resistant and clinical variants