Figure 2. Stable transgenic lines of S. ratti are established by microinjection of nucleic acid constructs followed alternating rounds of host and culture passage, selecting on expression of a fluorescent reporter gene product.
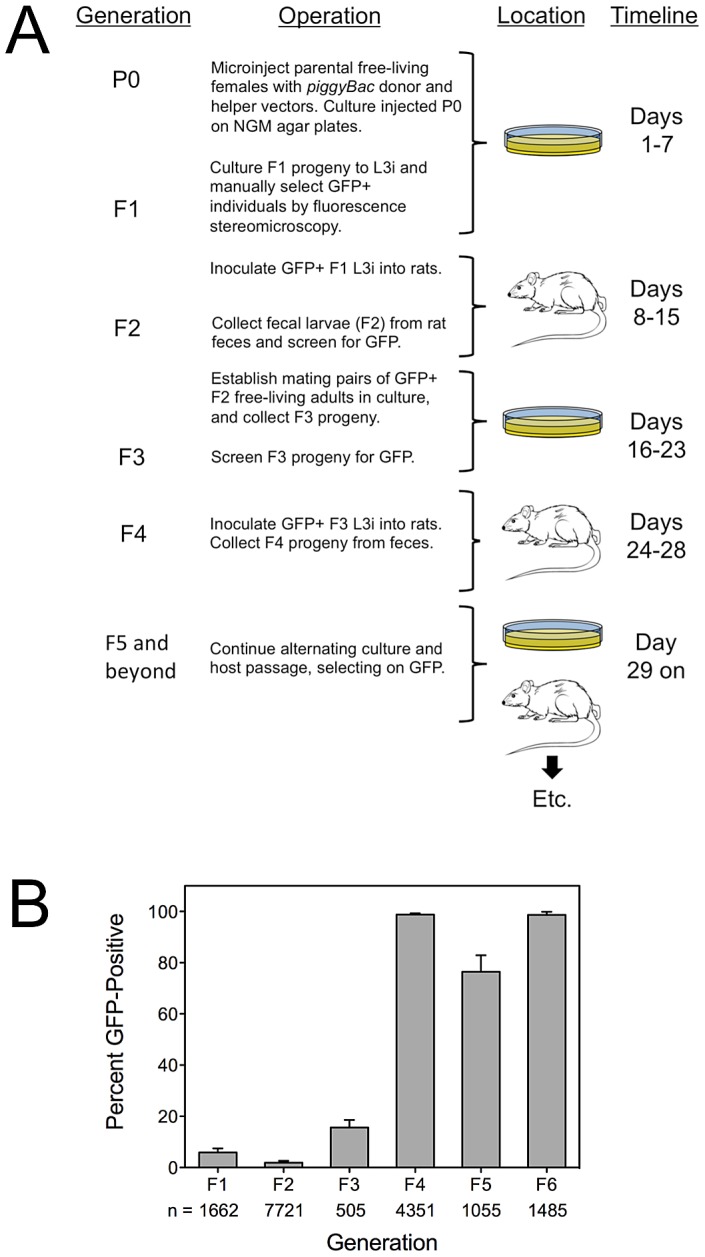
A) Diagram of major steps in isolation of stable transgenic lines of S. ratti. Initial gene transfer into parental (P0) free-living females is by gonadal microinjection of donor vectors alone or in combination with helper vector or capped transposase encoding mRNA. F1 larvae are derived in culture and screened for GFP expression. Transgene expressing individuals are reared to infective L3 (L3i) and inoculated into rats to establish as parasitic females. F2 progeny released in the feces of these rats are screened for transgene expression and positive larvae reared in culture to free-living males and females and allowed to mate. F3 progeny arising from these crosses are reared to L3i in culture in inoculated into rats. F4 progeny arising in the feces are screened for reporter transgene expression and used for further alternating rounds of culture and host passage with continued selection on GFP. The timeline indicates the intervals in days following microinjection of parental worms in which each generation is isolated up to the F5 when transmission and expression are generally stabilized. B) Frequency of transgene expressing progeny by generation during selection of stable transgenic lines of S. ratti. Data are mean (± one standard deviation) percentages of reporter transgene-expressing individuals in each generation of alternating host and culture passage with selection on GFP (see panel A). Means are derived from three independently established lines (PV2, PV3 and PV4). Sample sizes (n) indicated below the abscissa are totals of worms examined from all three lines. Statistics: in panel B, 2-way ANOVA, performed using Prism ver. 5.0c (GraphPad Software, Inc., La Jolla, California, USA), revealed a highly significant effect due to generation (P<0.0001) but no significant effect (P = 0.2) due to donor plasmid.
