Figure 3. Parasitic and free-living adults from a stable transgenic line of Strongyloides ratti express GFP in the body wall-specific manner expected for the Ss-act-2prom::gfp transcriptional reporter.
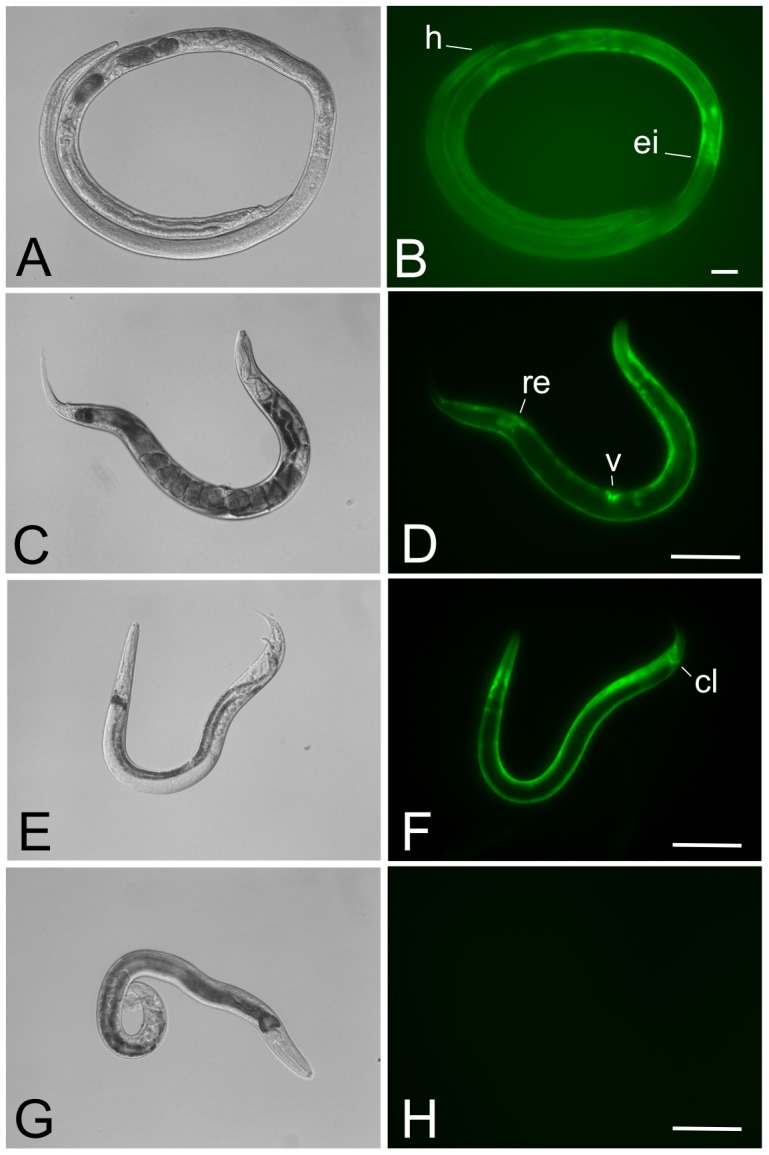
Typical patterns of GFP expression in parasitic female, free-living male and free-living female S. ratti expressing the integrated reporter transgene encoded in pPV356. (A, B) DIC and fluorescence images, respectively, of a parasitic female S. ratti from integrated line PV2. Note expression predominating in the body wall up to the level of the esophageal/intestinal boundary (ei). Position of the head is indicated (h). (C, D) DIC and fluorescence images, respectively, of a free-living female S. ratti from integrated line PV2. Note uniform expression throughout the body wall with additional loci of expression in the vulva (v) and rectum (re). (E, F) DIC and fluorescence images, respectively, of a free-living male S. ratti from transgenic line PV2. Note uniform expression in the body wall with additional expression in the cloaca (cl). (G, H) DIC and fluorescence images, respectively, of a non-transformed free-living male S. ratti. The fluorescence image in panel H was exposed for a period≥exposure times in panels B, D and F. Scale bar = 200 µm in all panels.
