Fig 2.
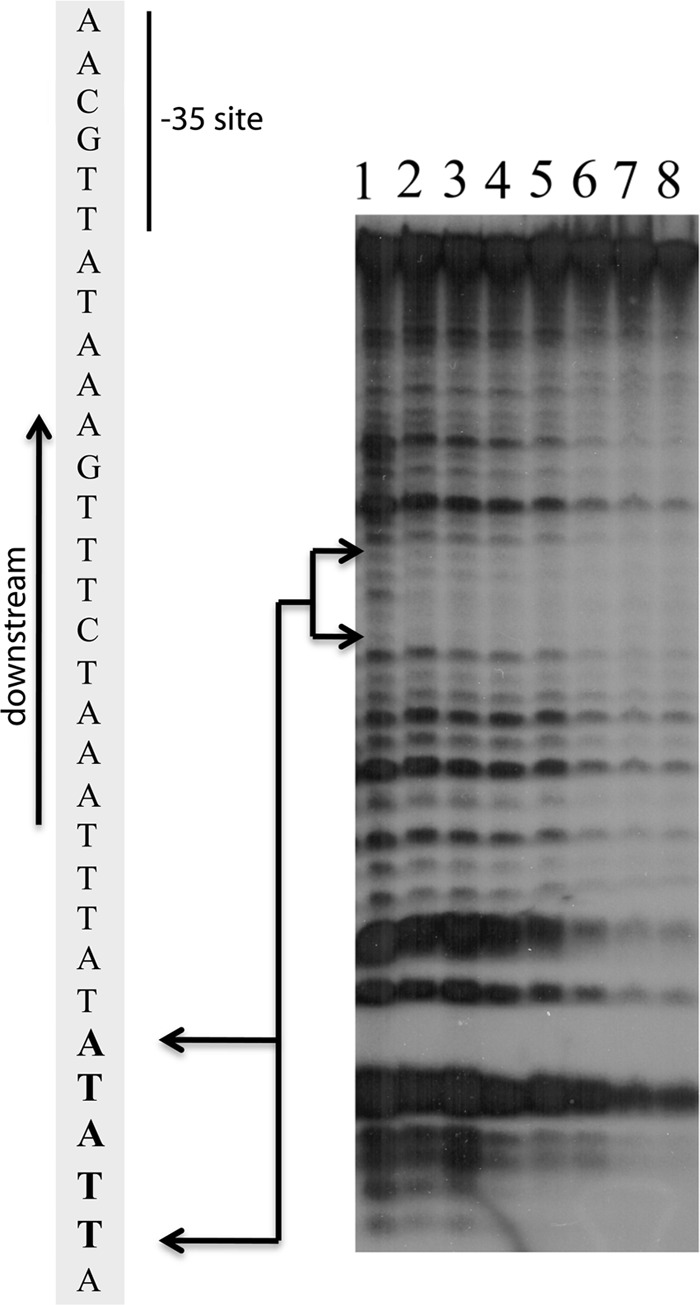
Identification of a high-affinity BpaB-binding site by DNase I footprinting. The illustrated representative experiment was conducted with the addition of increasing concentrations of BpaB to samples containing 5 ng 32P-labeled P50 erp operator noncoding dsDNA. Lanes 1 to 8 contained BpaB at final concentrations of 0, 4, 8, 10, 12, 15, 20, and 23 μM, respectively. The lower concentrations of BpaB protected the nucleotides TTATA from DNase1. Increasing protein concentrations led to expansion of protected nucleotides, consistent with EMSA data indicating the binding of additional BpaB molecules to DNA as the protein concentration increases (11, 30).
