Figure 2.
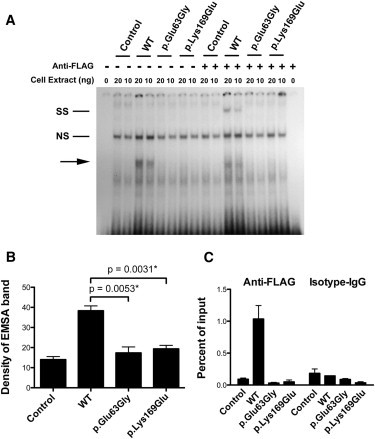
Functional Characterization of RBPJ Alterations Identified in AOS-Affected Families
(A) A representative EMSA from three independent experiments. The first lane shows a free probe derived from the HES1 promoter; subsequent lanes show nuclear protein extract (20 ng and 10 ng) that was prepared either from HEK 293T cells transfected with FLAG-tagged wild-type or mutant RBPJ or from untransfected HEK 293T cells as indicated. The shifted band corresponding to recombinant RBPJ constructs is labeled with an arrow. Super shift was performed by the addition of an antibody to the FLAG epitope expressed on the recombinant RBPJ proteins and is labeled in the figure as “SS.” A nonspecific band is labeled “NS.”
(B) We performed densitometric quantification of the EMSA bands from four independent experiments. The mean densities from untransfected HEK 293T cells and HEK 293T cells transfected with various RBPJ constructs are shown in the columns. Error bars represent the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Statistical differences between the means were calculated with the unpaired t test.
(C) ChIP was performed with anti-FLAG and anti-isotype control IgG on chromatin prepared from HEK 293T cells transfected with RBPJ constructs. Quantification of enriched DNA fragments was performed with quantitative RT-PCR with primers flanking a known RBPJ binding site in the HES1 promoter. Shown is a representative ChIP-qPCR from two independent experiments. Each experiment was composed of three technical replicates. Mean enrichment as a percentage of input chromatin is displayed. Error bars correspond to the mean ± SEM.
