Figure 1.
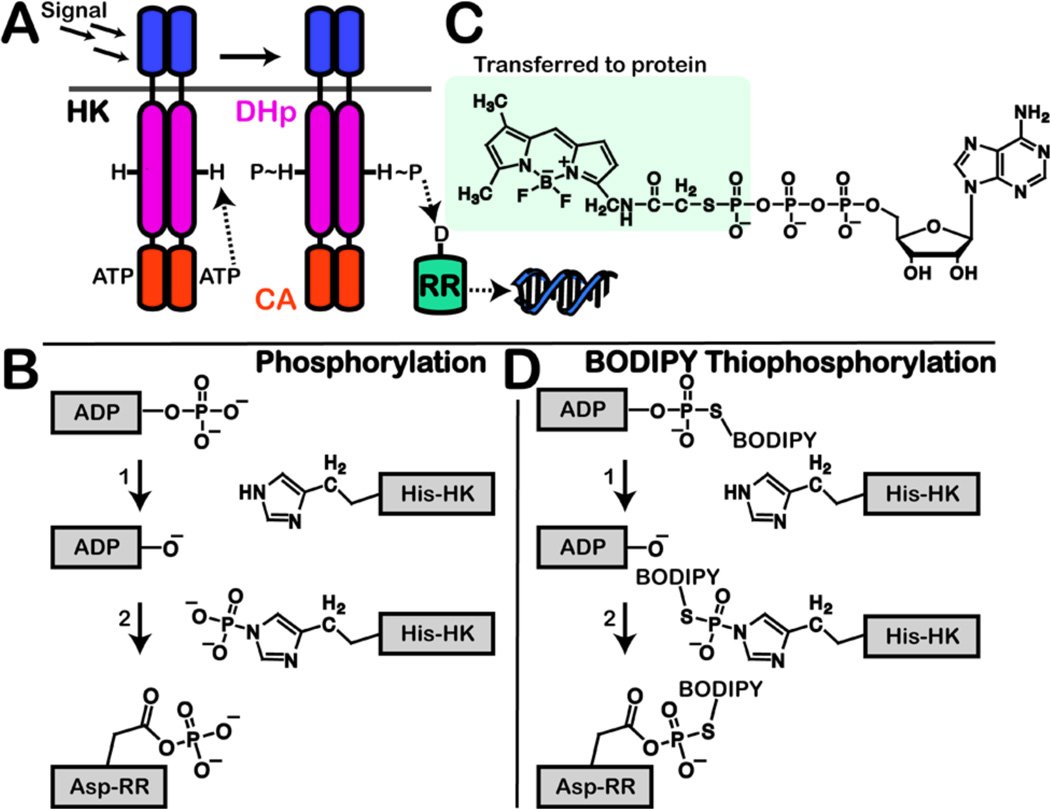
(A) HK is activated by an extracellular signal, which results in phosphorylation of a conserved histidine by ATP. The phosphoryl group is transferred to the aspartate on a RR. Activated RR then triggers a response, typically acting as a transcription factor. Domains: DHp, dimerization and histidine phosphotransfer; CA, catalytic and ATP-binding. (B) Mechanisms of HK autophosphorylation and phosphotransfer to RR. (C) Structure of B-ATPγS, highlighting the thiophosphate-BODIPY moiety that is transferred during autophosphorylation. (D) Proposed mechanism of B-ATPγS labeling of active HK and cognate RR.