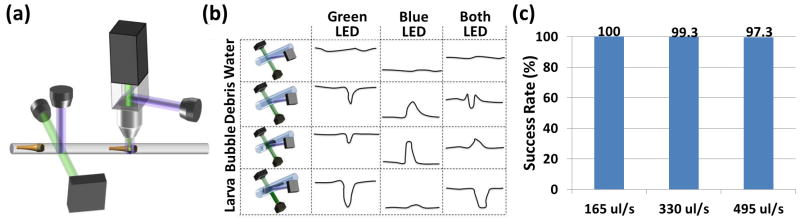
Fig. 3.
Zebrafish discriminator. (a) Schematic representation of the zebrafish discriminator. The system is composed of a bright-field discrimination system and a fluorescence-activated zebrafish sorter. (b) Schematic representation of the mechanism of action of the bright-field discrimination system. By combining both the scattered and transmitted signals the system distinguishes a zebrafish larva from air bubbles and debris. (c) Detection and discrimination reliabilities at increasing flow rates. The reliability is near 100 % at normal operating speeds of 330 μL/s. (n=150).