Figure 2.
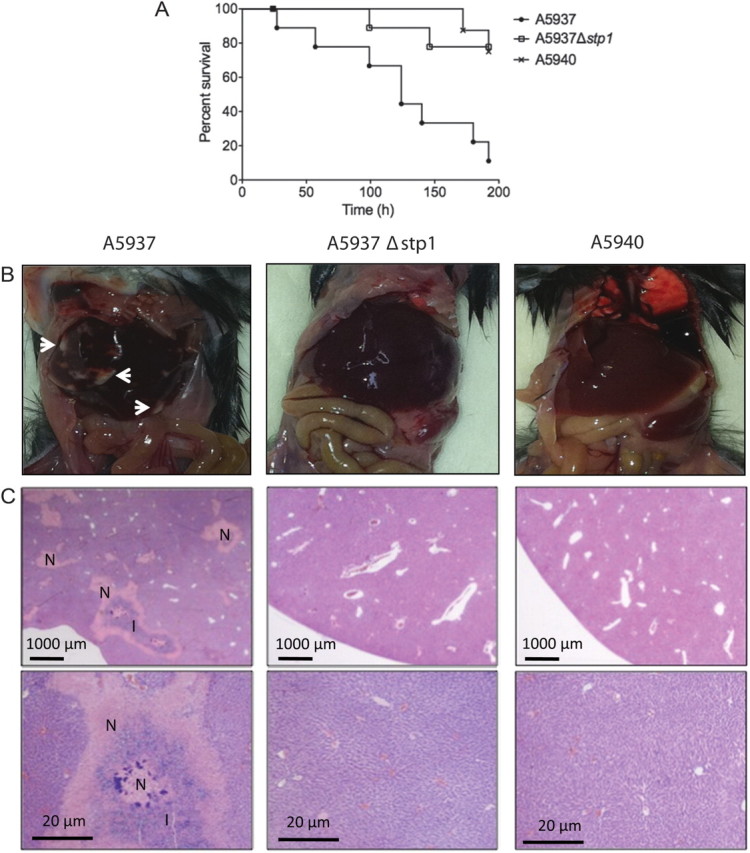
Deletion of stp1 results in attenuated virulence in Staphylococcus aureus. (A) Six-week-old C57BL/6J mice were injected with ∼1.0 × 108 bacterial cells. Kaplan-Meier curves indicate time to euthanasia for each strain. A5937 produced significantly more killing compared with both A5937Δstp1 and A5940 (P = .01; log-rank test). (B) Macroscopic and (C) histopathological analyses showed that the clinical vancomycin-susceptible parent strain (A5937) caused hepatic abscess formation and tissue necrosis, whereas this was not seen with the stp1 deletion mutant (A5937Δstp1) and the clinical vancomycin-intermediate S. aureus daughter strain (A5940). White arrows point to abscess formation in the liver; N represents severe necrosis; and I represents inflammatory infiltrate. Tissues were stained with hematoxylin and eosin.
