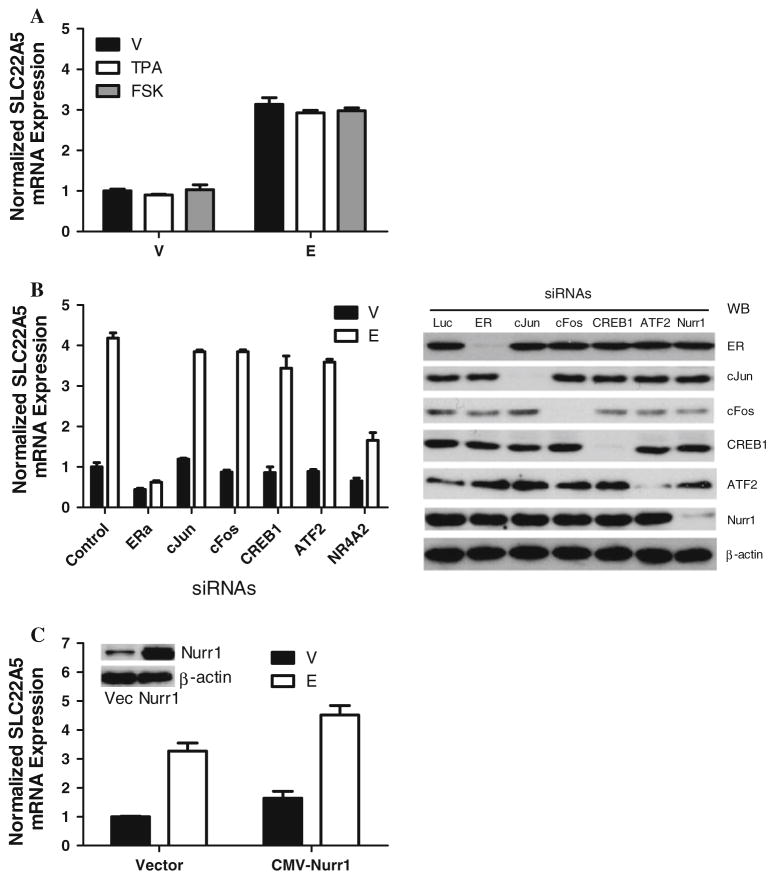
Fig. 4.
Effects of the AP-1, cAMP, and Nurr1 pathways on SLC22A5 expression. a Effect of small molecule chemicals for AP-1 and cAMP pathways on estrogen-induced SLC22A5 expression in MCF-7 cells. TPA or FSK was added with vehicle/E2 for 2 h. RNA was harvested and analyzed by qRT-PCR. b siRNA knockdown of ER, AP-1, CREB1, ATF2, or Nurr1 on estrogen-induced SLC22A5 expression. Hormone-depleted MCF-7 cells were transfected with siRNA against each gene, as indicated, for 36 h. The cells were then treated with vehicle/E2 for 2 h. The data for siLuc transfected and vehicle-treated samples were arbitrarily set as 1. The efficiency of the siRNAs has been validated to suppress the expression of target genes as shown in the Western blot. c Effect of Nurr1 overexpression on estrogen-induced SLC22A5 expression. Hormone-depleted MCF-7 cells were transfected with vector (vec) or CMV-Nurr1 plasmid for 36 h and then treated with vehicle/E2 for 2 h. RNA was harvested and analyzed by qRT-PCR. Inset verification of Nurr1 expression by Western blot