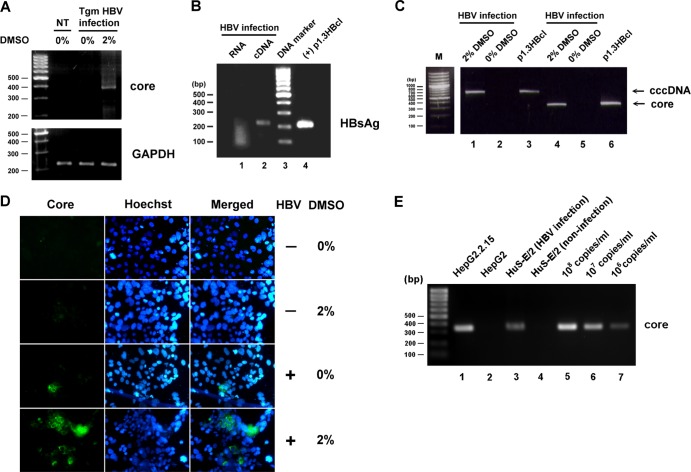
Fig 1.
HBV infection of DMSO-treated HuS-E/2 immortalized primary human hepatocytes. (A) HuS-E/2 cells were cultured for 12 days with 2% DMSO or were left untreated and were then incubated for 20 h with sera from HBV-transgenic mice (Tgm HBV infection); controls were DMSO-untreated cells not incubated with HBV (not treated [NT]). Infection was performed at a multiplicity of infection of about 5 HBV genome equivalents per cell. After removal of nonbound HBV, the cells were incubated for a further 12 days in the presence of 2% DMSO, and then RNA was isolated and amplified to detect the presence of HBV core protein mRNA. Control RT-PCRs were performed for endogenous GAPDH. The DNA markers are shown as molecular masses in 100-bp increments on the left. (B) DMSO-differentiated HuS-E/2 cells were incubated for 20 h with HBV concentrated from the culture medium of HepG2.2.15 cells grown for 12 days. Infection was performed at a multiplicity of infection of 10. RNA was then isolated and subjected to reverse transcription to generate cDNA, and PCR was performed to detect the presence of HBV HBsAg mRNA. Lane 1, PCR results for the RNA sample; lane 2, PCR results for the cDNA sample; lane 3, DNA markers; lane 4, positive control of plasmid p1.3HBcl (+). (C) Total DNA was isolated from HBV-infected DMSO-treated cells (lanes 1 and 4) or DMSO-untreated cells (lanes 2 and 5) and subjected to PCR to detect the presence of HBV cccDNA (lanes 1 and 2) or core protein DNA (lanes 4 and 5). Lanes 3 and 6, positive-control plasmid p1.3HBcl. (D) HuS-E/2 cells seeded on 18-mm coverslips were treated for 12 days with 2% DMSO or were left untreated and were then incubated with HBV for 20 h, washed, and incubated for an additional 12 days with or without 2% DMSO. Viral infection was then examined by indirect immunofluorescence staining using monoclonal anti-core protein antibody (left) and Hoechst 33258 (center), applied at the same time as the secondary antibody to label the nucleus. The stained cells were visualized by fluorescence microscopy. (E) Total DNA was isolated from the 100-fold-concentrated culture medium from HepG2.2.15 cells (lane 1), HepG2 cells (lane 2), HBV-infected DMSO-treated cells (lanes 3), or noninfected DMSO-treated cells (lane 4) and subjected to PCR to detect the HBV genomic DNA. Lanes 5 to 7, serial dilutions of a known amount of plasmid p1.3HBcl as standard.