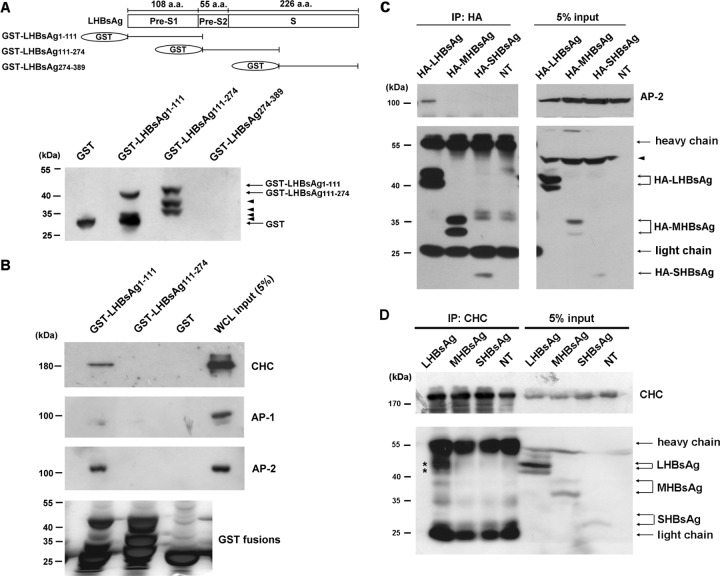
Fig 4.
Interaction between LHBsAg and CHC or AP-2. (A) (Top) Schematic representation of the amino acid (a.a.) residues within the LHBsAg subdomains, designated pre-S1, pre-S2, and S; (bottom) Western blot results when LHBsAg cDNA fragments coding for amino acids 1 to 111, 111 to 274, or 274 to 389 were cloned into pGEX-6p-1 for expression in E. coli and purification as GST fusion proteins and antibodies against GST were used to detect the expression of the GST fusion proteins. Arrowheads, leaky expression of proteins. (B) GST pulldown assay. GST-LHBsAg fusion proteins or GST bound to glutathione-Sepharose 4B beads were incubated with lysates of HuS-E/2 cells, and then, after GST pulldown, Western blot analysis was performed using antibodies against CHC, AP-1, AP-2, or GST. The positions of molecular mass markers are shown on the left. (C and D) Coimmunoprecipitation and Western blot analysis. HuS-E/2 cells were transfected with plasmid pcDNA3.0-HA-LHBsAg, pcDNA3.0-HA-MHBsAg, or pcDNA3.0-HA-SHBsAg coding, respectively, for HA-tagged LHBsAg, MHBsAg, or SHBsAg, and then, at 2 days posttransfection, the cells were harvested and subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with antibodies specific for HA (C) or CHC (D), followed by Western blot analysis with antibodies against HA, AP-2, or CHC, as indicated. NT, nontransfected cells. The molecular mass markers are indicated on the left. Asterisks, proteins coimmunoprecipitated with CHC; arrowheads, nonspecific bands.