Fig 5.
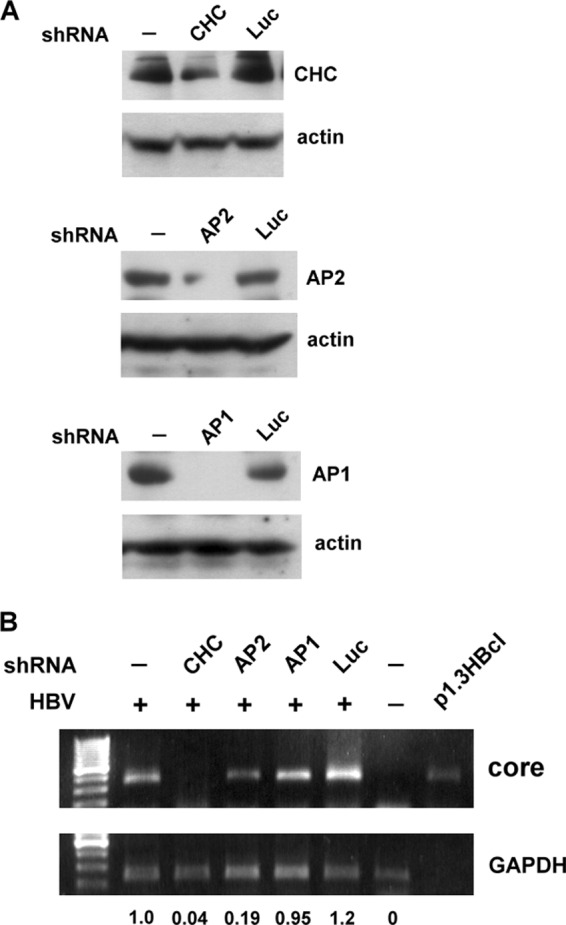
shRNA-mediated knockdown of CHC or AP-2 inhibits HBV infection. (A) shRNA knockdown of CHC, AP-2, or AP-1. DMSO-treated HuS-E/2 cells were transfected with plasmids expressing shRNAs specific for CHC (top), AP-2 (center), or AP-1 (bottom); cells transfected with plasmid containing shRNA against luciferase (Luc) served as controls. At 2 days posttransfection, Western blot analysis was performed using antibodies against CHC, AP-2, or AP-1, as indicated, with actin as the internal control. (B) Effect of CHC, AP-2, or AP-1 knockdown on HBV infection. DMSO-treated HuS-E/2 cells were transfected with shRNAs against CHC, AP-2, or AP-1 as described for panel A, and then at 2 days posttransfection were subjected to HBV infection or left untreated. At 12 days postinfection, RNA was isolated from the infected cells and subjected to reverse transcription and PCR analysis to detect HBV core protein mRNA. Plasmid p1.3HBcl served as the positive control. Relative expression levels of core mRNA are shown.
