Fig 2.
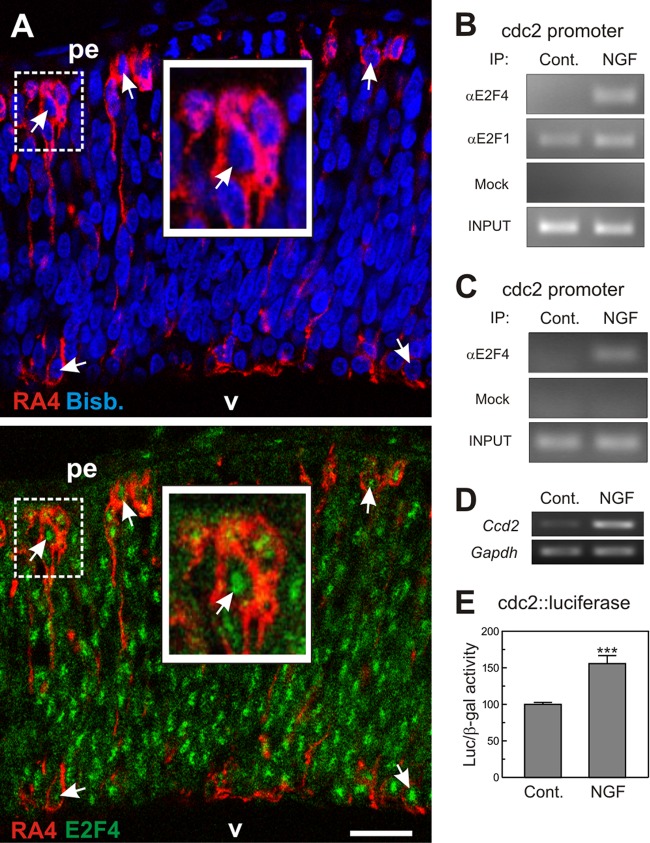
Interaction of E2F4 with the cdc2 promoter in DCRNs. (A) E6 chick retina cryosection (12 μm) immunolabeled for E2F4 (green) and the RGC-specific marker RA4 (red) and counterstained with bisbenzimide (blue) to reveal the nuclei. Arrows indicate the E2F4-specific immunostaining in the nuclei of RA4-positive neurons. pe, pigment epithelium; v, vitreus body. The insets show high-magnification images of the dashed squares. Bar, 30 μm. (B) ChIP analysis of the occupancy of the chick cdc2 promoter by E2F4 and E2F1 in DCRNs cultured for 30 min either in the presence (NGF) or absence (Control) of NGF. The anti-E2F4 antibody C-108 (αE2F4), the anti-E2F1 antibody C-20 (αE2F1), or irrelevant (Mock) antibodies were used for immunoprecipitation. INPUT, RT-PCR amplification from extracts before immunoprecipitation. (C) ChIP analysis performed with a rabbit polyclonal anti-E2F4 antibody from Bethyl Laboratories (αE2F4) or irrelevant (Mock) antibodies. See panel B for details. (D) RT-PCR analysis of cdc2 expression in DCRNs treated for 15 h with NGF (+) or vehicle (−). Gapdh was used as a control. (E) Luciferase activity, normalized to β-galactosidase, in extracts from DCRNs cotransfected with β-galactosidase and cdc2-luciferase, and treated for 16 h with NGF or vehicle. ***, P < 0.005 (Student t test; n = 3).