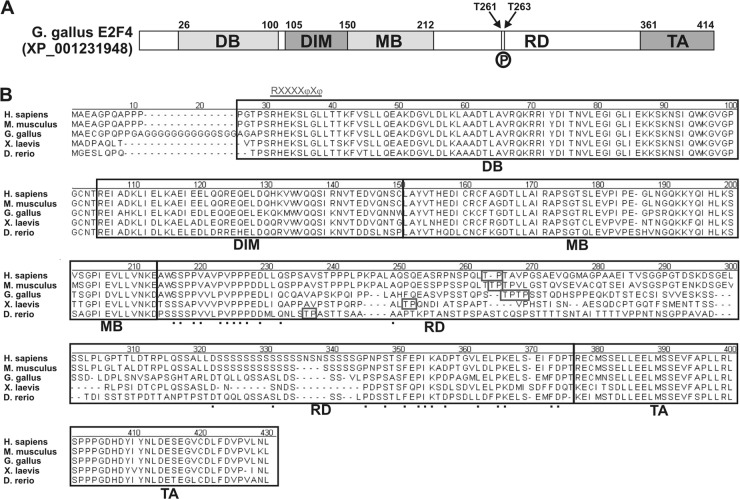
Fig 9.
Structure and functional domains of the E2F4 transcription factor. (A) Chick E2F4 can be divided into different functional domains: the DNA-binding domain (DB), the E2F/DP dimerization/marked box domains (DIM/MB), the regulatory domain (RD) described in the present study, and the transactivation domain (TA). Numbers indicate the amino acid positions of the transition between different domains. Arrows indicate the positions of Thr261 (T261) and Thr263 (T263), which are susceptible to be phosphorylated by p38MAPK (P). (B) Amino acid sequence comparison of the E2F4s from human E2F4 (Homo sapiens; accession number NP_001941), mouse E2F4 (Mus musculus; accession number NP_683754), chick E2F4 (Gallus gallus; accession number JQ678847), Xenopus laevis E2F4 (X. laevis; accession number NP_001086706), and zebrafish E2F4 (Danio rerio; accession number AAH56832). Alignment was performed by the CLUSTAL method to identify contiguous regions of homology. Black boxes indicate the different domains mentioned above. Boxes indicate the Thr residues susceptible to be phosphorylated by p38MAPK, as predicted by NetPhosK 1.0 software. Underlined characters indicate the consensus sequence for the p38MAPK docking site, R/KXXXXφXφ, where “φ” represent hydrophobic residues (11). Such a domain can be observed at the beginning of the DB domain. Dots represent conserved amino acids within the regulatory domain (RD).