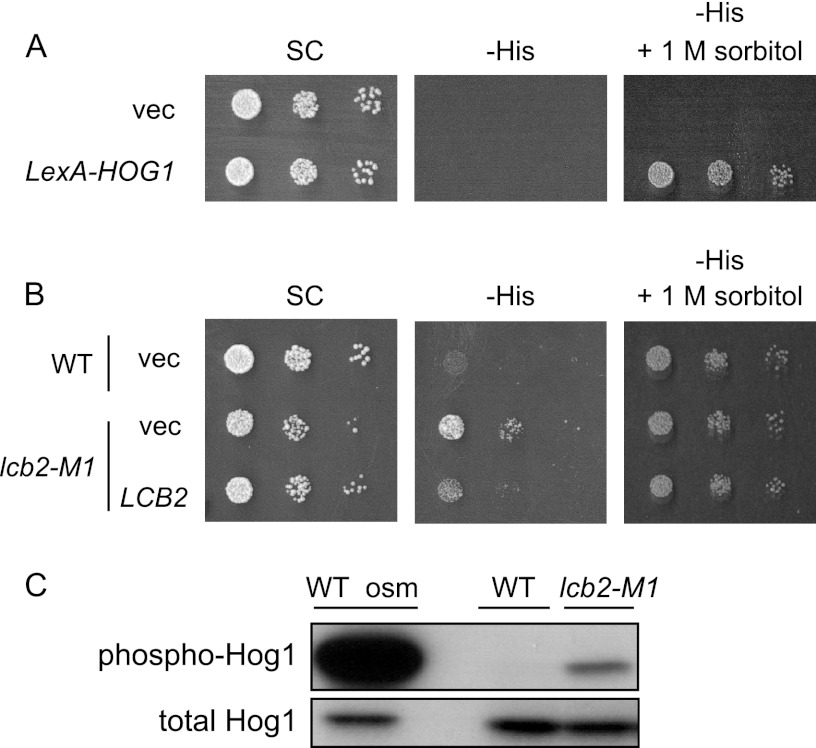
Fig 2.
Screen for mutants exhibiting constitutive activation of the HOG pathway. (A) The parental strain, which has a LexAop-HIS3 reporter gene and a LexA-Hog1 expressing plasmid, grows on His-depleted medium in an osmotic stress-dependent manner. TM415, harboring the vector (p414-LexA) or the LexA-HOG1 coding plasmid (pMT304), was spotted onto SC-Trp (SC), SC-Trp His (-His), and SC-Trp His supplemented with 1 M sorbitol (-His + 1 M sorbitol) plates and incubated for 2 days at 30°C. (B) The lcb2-M1 mutant cells grow on the -His plate in the absence of osmotic stress. Wild-type (TM415, WT) and lcb2-M1 (MH266) cells, harboring pMT304 and a vector (pRS416) or an LCB2 plasmid (pMH29), were spotted onto SC-Trp Ura (SC) and SC-Trp His Ura (-His) plates and incubated for 2 days at 30°C. (C) lcb2 mutant cells exhibit elevated Hog1 phosphorylation. Phosphorylated Hog1 in wild-type (TM141) and lcb2-M1 (MH280) cells was detected by Western blotting using an anti-phospho-p38 specific antibody. Wild-type cells treated with 0.4 M KCl for 3 min (WT osm) were used as a positive control.