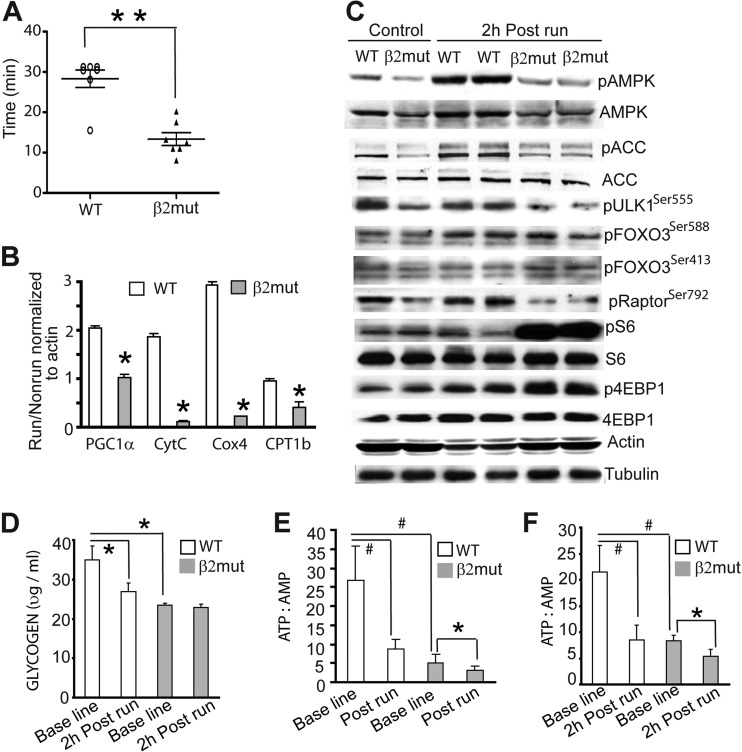
Fig 7.
Poor exercise endurance in β2 mutant animals. (A) Performance of WT and β2 mutant animals in the treadmill running assay (n = 7 for each group). **, P < 0.0001. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of gastrocnemius muscle from WT and β2 mutant mice 6 h after and before the treadmill run. For each group, data were normalized to β-actin expression. *, P < 0.05. (C) Immunoblot analysis of pAMPK, pACC, pRaptor, pULK1, pFOXO3, p4EBP1, pS6, total S6, and total 4EBP1 in gastrocnemius muscle from WT and β2 mutant mice showing basal and exercise-induced levels of AMPK activation. Note that total AMPK but not total ACC levels were reduced in β2 mutant animals. β-Actin and tubulin were used as loading controls. (D to F) Glycogen content at baseline and 2 h postrun (D) and ATP/AMP ratio at baseline and immediately after run (E) and 2 h postrun (F) in the epitrochlearis muscle of WT and β2 mutant animals. *, P < 0.03; #, P < 0.01.