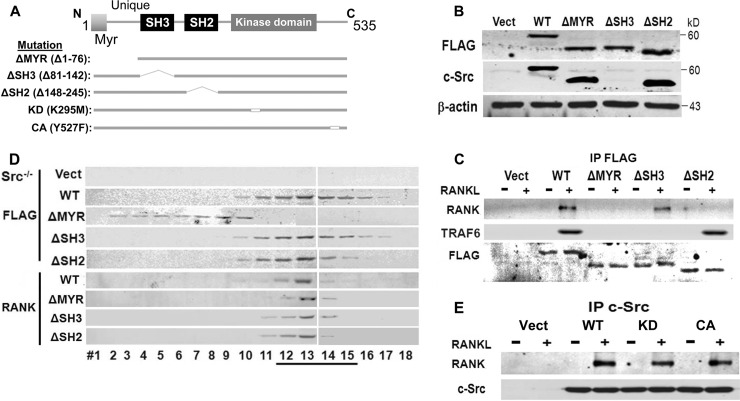
Fig 2.
c-Src N-terminal myristoylated region and SH2 domain mediate RANK association. (A) WT and mutated c-Src constructs. (B) Lysates of c-Src−/− splenic macrophages, retrovirally transduced with empty vector or FLAG-tagged WT, ΔMYR, ΔSH3, or ΔSH2 c-Src, were immunoblotted with anti-FLAG or anti-c-Src MAb. (C) Cytokine-starved c-Src−/− preosteoclasts, retrovirally transduced with empty vector (Vect) or FLAG-tagged WT, ΔMYR, ΔSH3, or ΔSH2 c-Src, were maintained ± RANKL for 30 min. FLAG immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted for RANK, TRAF6, or FLAG. (D) Cytokine-starved c-Src−/− preosteoclasts, transduced with vector or FLAG-tagged WT, ΔMYR, ΔSH3, or ΔSH2 c-Src, were treated ± RANKL for 30 min. Lysates were subjected to gradient centrifugation, and the fractions were immunoblotted for FLAG or RANK. (E) c-Src−/− preosteoclasts, transduced with vector or WT, kinase-inactive (KD) or constitutively active (CA) c-Src, were maintained ± RANKL for 30 min. c-Src immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted for RANK or c-Src. Results are representative of three independent experiments.