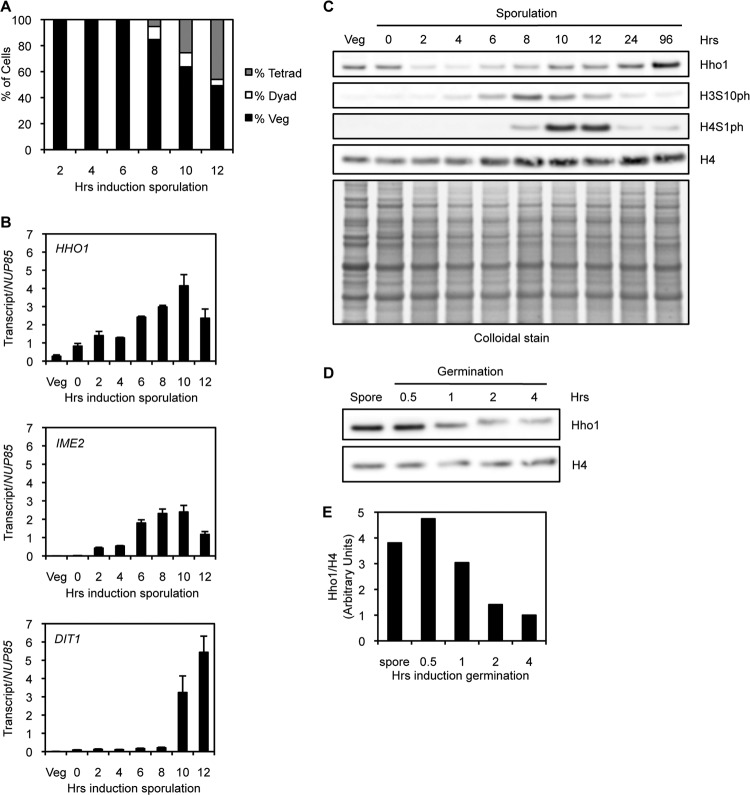
Fig 2.
Hho1 is depleted in meiotic yeast and enriched in mature spores. (A) A sporulation time course indicates the percentage of cells/asci with a single nucleus (vegetatively growing), two nuclei (dyad), or three or more nuclei (tetrad). Diploid yeast cells are deprived of nutrients, induced to enter sporulation synchronously, and stained with DAPI at different times postinduction. Meiotic divisions begin at approximately 8 h after induction of sporulation. (B) RT-qPCR of RNA from yeast harvested at different times over the course of sporulation. HHO1 is transcribed at a basal level in vegetatively growing yeast (Veg), but its transcription increases over the course of meiosis. The HHO1 transcription pattern is similar to that of an early meiotic gene (IME2) and temporally distinct from that of a late meiotic gene (DIT1). NUP85 is used as a control transcript for all time points. (C) Western blot analysis of protein extracts from yeast harvested at different times over the course of sporulation. Hho1 protein levels decrease dramatically during early meiosis and peak in mature spores. H3S10ph marks meiotic divisions, and H4S1ph marks the beginning of postmeiotic compaction. Total histone H4 and a colloidal stain of total protein are used as loading controls. (D) Western blot analysis of protein extracts from yeast harvested at different times over the course of germination. Cell division begins at 4 h after induction of germination. Hho1 protein levels decrease during germination as spores reenter the cell cycle. Total histone H4 is used as a loading control. (E) Quantification of the Western blot in panel D. Hho1 protein levels are normalized to H4 protein levels. The ratio in vegetative yeast (4 h after induction of germination) is set to 1.