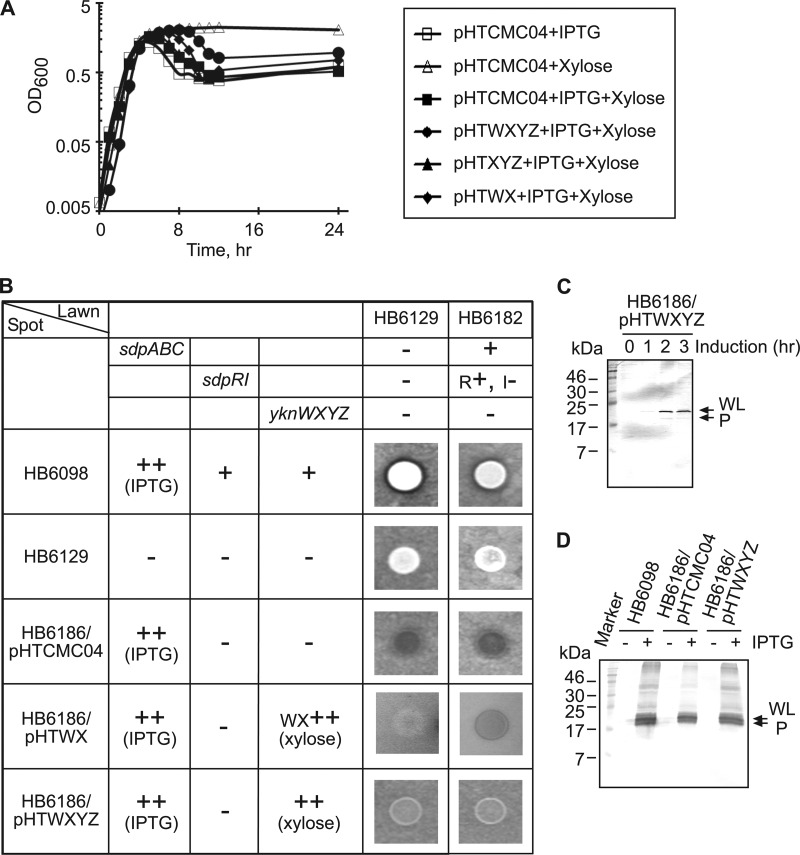
Fig 3.
Protection of B. subtilis cells from the SDP-dependent self-lysis. (A) B. subtilis HB6186 (Pspac-hy-sdpABC sdpI∷mls yknWXYZ∷Kan) carrying pHTCMC04 vector or its derivatives containing yknWXYZ (pHTWXYZ), yknWX (pHTWX), and yknXYZ (pHTXYZ) were grown to mid-exponential phase and diluted 1:50 into DSM either with or without 1 mM IPTG and 0.5% xylose. (B) B. subtilis cells were spotted onto agar plates containing either HB6129 (sdpABC-sdpRI∷tet yknWXYZ∷Kan) or the HB6182 (sdpI∷mls yknWXYZ∷Kan) lawn strain, and plates were supplemented with 1 mM IPTG and 0.5% xylose to induce the production of SDP and Ykn (indicated by ++), respectively. Inhibition zones were detected after 10 h of incubation at 37°C. +, present; −, absent; R+, sdpR present; I−, sdpI absent. (C) Expression of SdpC in cells overproducing Ykn proteins. HB6186 cells carrying the pHTWXYZ plasmid (HB6186/pHTWXYZ) were supplemented with 1 mM IPTG and 0.5% xylose and incubated for 3 h. Protein (10 μg total) was separated by 16% SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-SdpC antibody. WL, whole length; P, processed. (D) Effect of YknWXYZ overproduction on the secretion of SdpC. Secreted proteins were precipitated by 10% trichloroacetic acid (TCA) from 10 ml of culture supernatants of indicated cells. Proteins were separated by 16% SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-SdpC antibody. WL, whole length; P, processed.