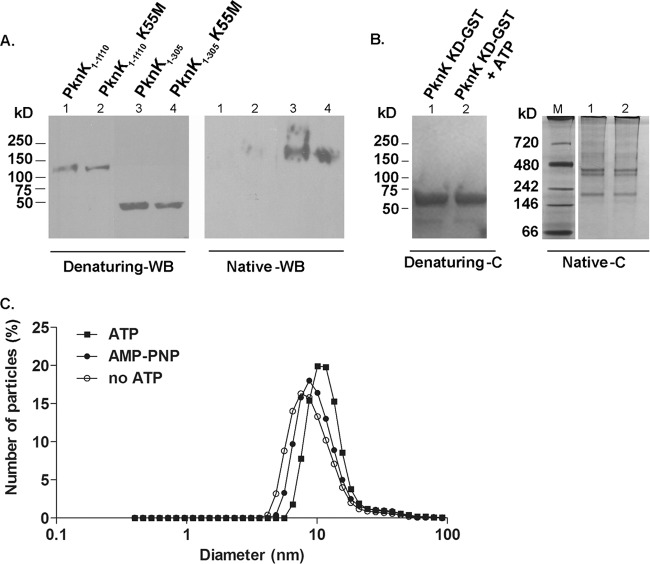
Fig 6.
PknK forms oligomeric complexes in solution. (A) Western blot (WB) analysis with anti-PknK antibody of IVTT-synthesized PknK1-1110 and PknK1-305 wild type and their K55M counterparts simultaneously resolved on native and denaturing 4 to 15% gradient polyacrylamide gels. Denaturing gel WB analysis showed the linear size of the proteins, whereas WB analysis of the native gel revealed the formation of an oligomer with the wild-type and mutant PknK1-305 proteins. (B) PknK KD-GST forms oligomers of various sizes in solution. A Coomassie-stained gel (C) shows the effect of ATP on the oligomerization pattern of PknK KD-GST (5 μg) after kinase assay with 1 mM ATP, followed by resolution on a native and denaturing 4 to 15% gradient polyacrylamide gel. The presence of ATP did not reveal any changes in the oligomerization pattern of PknK KD-GST. Lane M, native molecular mass protein marker. (C) Effects of ATP binding and hydrolysis on the PknK KD-GST particle size. Dynamic light scattering measurements were made on PknK KD-GST after in vitro kinase assay with 1 mM ATP or AMP-PNP (a nonhydrolyzable ATP analog) and compared with a PknK KD-GST (minus ATP) control. The data are presented as the change in diameter of the particle in solution. In comparison to the control, the particle size increased by ∼56% in the presence of ATP. The change in the diameter of the particle from 7.5 nm (control) to 11.7 nm (with ATP) is indicated by a shift on the x axis. In contrast, the change in particle size with AMP-PNP was minimal.