Fig 1.
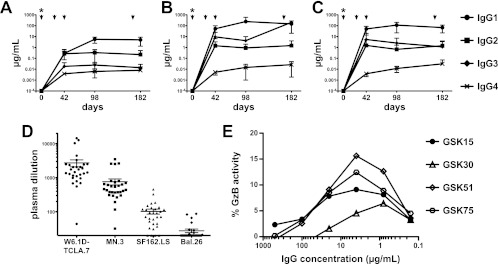
Plasma antibody activity induced by GSK PRO HIV-002. (A to C) Vaccine-induced reactivity by isotype. Serial serum samples from vaccine recipients were analyzed for vaccine-specific antibody. Binding antibody multiplex assay data are plotted as estimated antibody concentrations for IgG subclasses; asterisks indicate that antibodies at day 0 were below the limit of detection. IgG subclass responses to HIV-1 gp120 appeared at day 42, with IgG1 responses peaking at day 98 (A). Antibody responses to Nef (B) and Tat (C) also appeared at day 42. The overall concentrations of HIV-1-specific antibody responses mirror the relative concentrations present in blood. (D) Neutralization activity of d182 serum. Serum samples were tested for activity against a panel of Env-pseudotyped viruses in the TZM-bl assay. No neutralizing activity was detected at a 1:20 dilution of preimmunization samples. In contrast, serum samples from day 182 showed neutralization of autologous W6.1D-TCLA.7 Env-pseudotyped virus (geometric mean titer, 1:1645) and neutralization against HIV-1 MN.3 (geometric mean titer, 1:448) in all vaccine recipients. Most vaccine recipients (26/30, or 87%) developed neutralizing activity against HIV-1 SF162.LS (geometric mean titer, 1:75) while a minority developed activity against HIV-1 BaL.26 (9/30, or 30% of subjects with neutralizing activity). (E) ADCC activity of serum IgG. Serum IgG from the four subjects (identified by GSK numbers) from whom rMAbs were recovered was tested for ADCC activity as described. No activity was detected in samples prior to immunization. In contrast, ADCC activity was detected in all samples from day 182 with a peak in granzyme B (GzB) activity comparable to activity levels of the recovered rMAbs (Fig. 4).