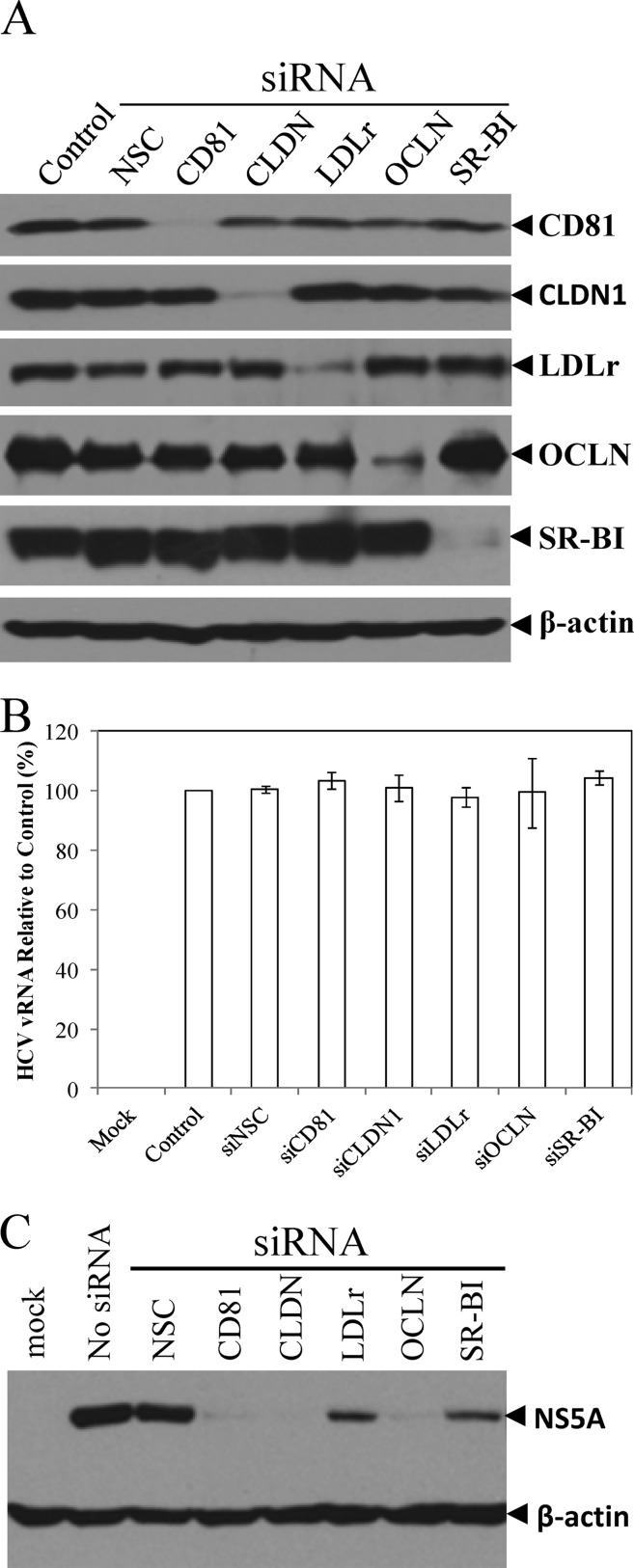
Fig 5.
Effects of siRNA-mediated knockdown of key HCV receptors on HCV attachment and infection. Huh-7.5 cells in 12-well plates were transfected with 0.2 nmol of each siRNA specific to CD81, claudin-1, LDLr, occludin, and SR-BI using RNAiMax reagent (Invitrogen) as described in Materials and Methods. (A) At 48 h p.t., the levels of CD81, claudin-1, LDLr, occludin, and SR-BI expression were determined by Western blotting using specific antibodies to each protein as indicated on the right. (B) Effects of silencing CD81, claudin-1, LDLr, occludin, and SR-BI expression on HCV attachment. At 48 h after siRNA transfection, Huh-7.5 cells were incubated with HCV at 37°C for 2 h. Upon extensive washing, total cellular RNA was extracted with RNAzol reagent. The levels of HCV vRNA were quantified by qRT-PCR and were converted to a percentage of the control with 100% representing the level of HCV vRNA without antibody treatment. Average levels of HCV vRNA and deviations from three independent experiments are shown. (C) Effects of the siRNA-mediated knockdown of the above receptors on HCV infection. At 48 h after siRNA transfection, Huh-7.5 cells were incubated with HCV on ice for 2 h, followed by extensive washing. The HCV-attached Huh-7.5 cells were incubated at 37°C for 24 h. HCV NS5A in the cell lysates was detected by Western blotting using β-actin as a control.