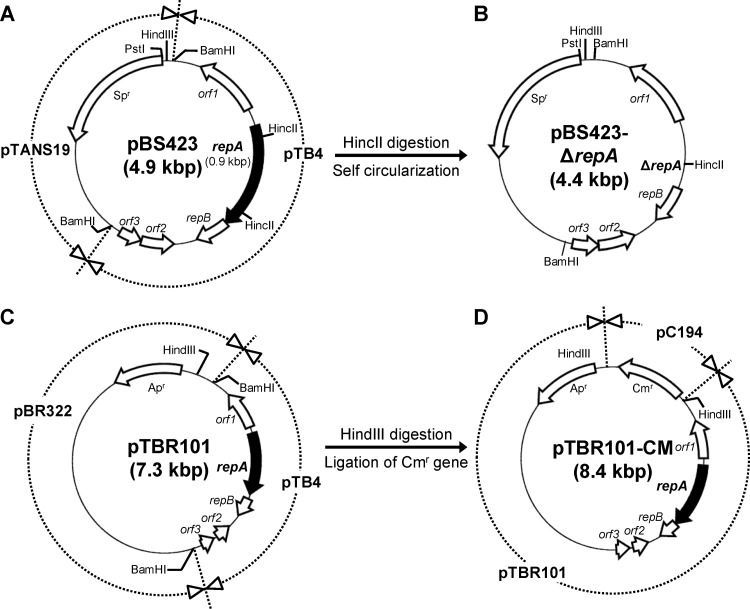
Fig 2.
Structures of the plasmids used in markerless gene deletion. Genes are identified by open arrows, except for the repA gene, which is identified by black arrows. Representative restriction sites in the plasmids are shown. DNA regions in plasmids pBS423 (A), pTBR101 (C), and pTBR101-CM (D) are shown in the surrounding circle (dashed lines) of each plasmid and are divided according to the source of the DNA region. Names of derived genetic materials are shown on the surrounding circle. (A) The E. coli-Bifidobacterium shuttle vector pBS423 was constructed by cloning the cryptic plasmid pTB4 from B. longum BK25 into the BamHI site of pTANS19. (B) The conditional replication vector pBS423-ΔrepA was constructed by the self-circularization of the 4.4-kbp HincII fragment of pBS423. Because pBS423-ΔrepA lacks the repA gene, which encodes the replication initiation protein RepA, it cannot replicate in B. longum 105-A. (D) To construct pTBR101-CM, which is incompatible with pBS423-ΔrepA, a chloramphenicol resistance gene (Cmr) from pC194 (cryptic plasmid of Staphylococcus aureus) was cloned into the HindIII site of pTBR101 (C), which consists of pTB4 from B. longum BK25 and pBR322. Spr, spectinomycin resistance gene; Apr, ampicillin resistance gene.