Fig 3.
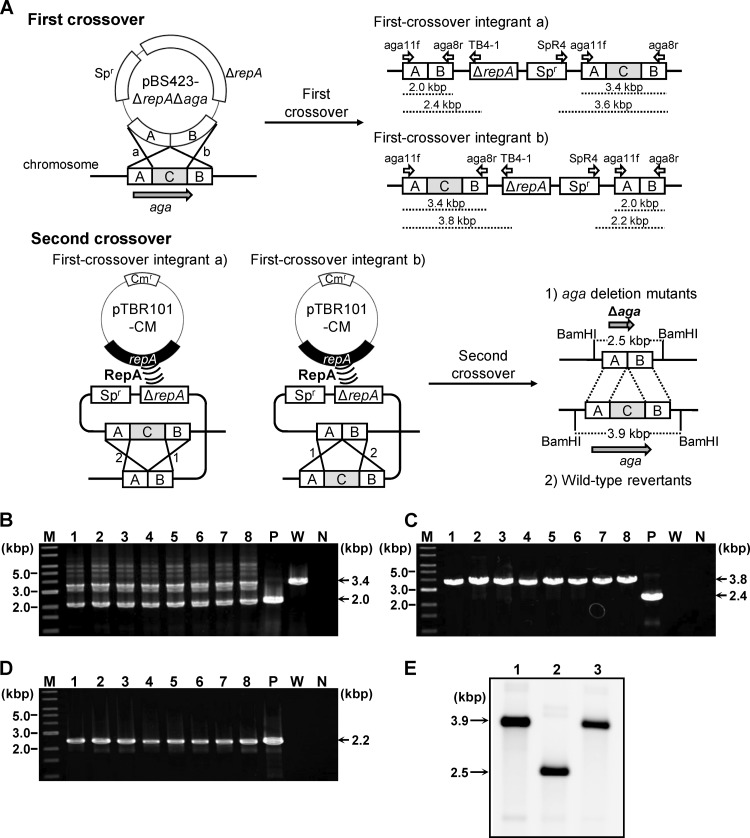
(A) Schematic of the markerless gene deletion procedures conducted in B. longum 105-A. The first crossover event is shown in the upper panel, and the second crossover event is in the lower panel. The first crossover between the target gene (aga) and the conditional replication vector pBS423-ΔrepAΔaga, harboring the Δaga allele, which lacks the internal region of aga (C in the chromosome structure), can take place with homologous region A or B, yielding two types of first-crossover integrants, designated a and b. Primers used to check the genotypes of first-crossover integrants are shown as open arrows, with names above the predicted structure of the target locus of each first-crossover integrant. The expected lengths of the amplicons generated using these primers are indicated by dashed lines below the predicted structures. The second crossover event, facilitated by the supply of RepA by the plasmid pTBR101-CM, can take place with homologous region A or B in the first-crossover integrants, designated a and b. The second crossover event yielded two types of strains, aga deletion mutants and wild-type revertants. Predicted restriction sites for BamHI and the predicted lengths of the restriction fragments are indicated in the structure of the aga locus for each strain. (B to D) Genotype analyses of the pBS423-ΔrepAΔaga transformants to confirm integration of pBS423-ΔrepAΔaga into the aga locus. Amplified fragments produced using the aga11f/aga8r primer pair (B), the aga11f/TB4-1 primer pair (C), and the SpR4/aga8r primer pair (D) were subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis. A 1-kb DNA ladder (New England BioLabs, Inc., Ipswich, MA) was used as a molecular mass marker (lane M). The sizes of representative marker fragments are shown to the left of each panel. Each lane shows amplified DNA generated from a DNA template: lanes 1 to 8, candidate first-crossover integrants; lane P, pBS423-ΔrepAΔaga (positive control for amplification); lane W, B. longum 105-A (wild-type); and lane N, no template DNA (negative control for amplification). The sizes of the amplified fragments are shown to the right of each panel. (E) Southern hybridization analysis of markerless aga deletion. Samples of BamHI-digested chromosomal DNA (4 μg) were electrophoresed in a 0.7% agarose gel. Each lane corresponds to a DNA sample from a Bifidobacterium strain: lane 1, B. longum 105-A; lane 2, 105-A Δaga; lane 3, wild-type revertant (after the second crossover). Electrophoresed total DNA was transferred to a nylon membrane. The 3′ region of aga (region B in panel A) was used as a probe. Hybridization signals were detected after exposure for 30 min. The sizes of the hybridized fragments are indicated to the left of the panel.