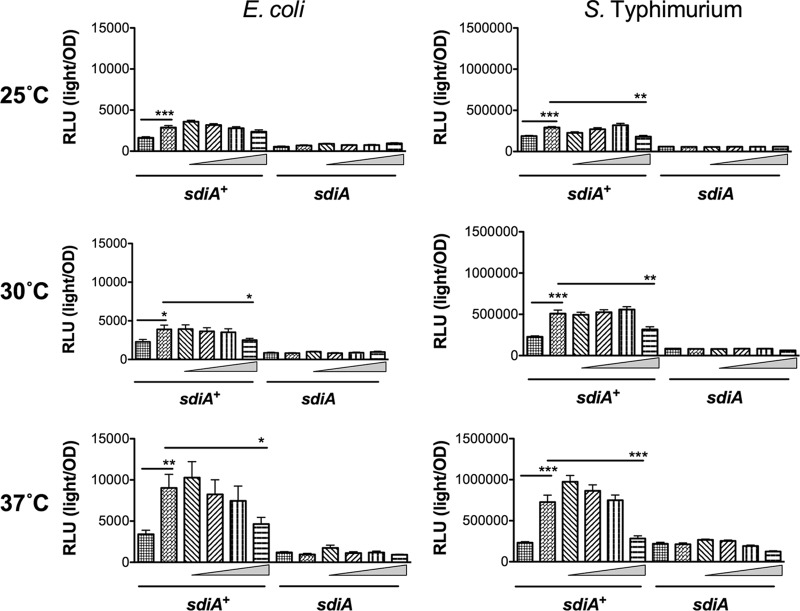
Fig 10.
Indole inhibits AHL detection by SdiA of E. coli K-12 and S. Typhimurium during standing growth conditions. (A) Expression of the gadW::Tn5-luxCDABE fusion in E. coli K-12 in either the wild-type (AL4001), sdiA mutant (JLD800), tnaA mutant (ME021), or tnaA sdiA double mutant (ME020) background. (B) Expression of the srgE-luxCDABE fusion in S. Typhimurium 14028 or the sdiA mutant (BA612). Relative light units (light/OD590) after 9 h of growth with shaking are indicated by bars for 0.1% ethyl acetate (EA) and 0.5% dimethylformamide (DMF) (hatched), 100 nM AHL + 0.5% DMF (bricked lines), 100 nM AHL + 1 μM indole (diagonal downward-slanting lines), 100 nM AHL + 10 μM indole (diagonal upward-slanting lines), 100 nM AHL + 100 μM indole (vertical lines), 100 nM AHL + 1 mM indole (horizontal lines). Each data point is the average for nine biological replicates, and error bars indicate SEM. Statistical significance in comparison to results with the solvent control or the AHL + solvent control is denoted by asterisks representing t test P values: ∗, <0.05; ∗∗, <0.005; ∗∗∗, <0.0005.