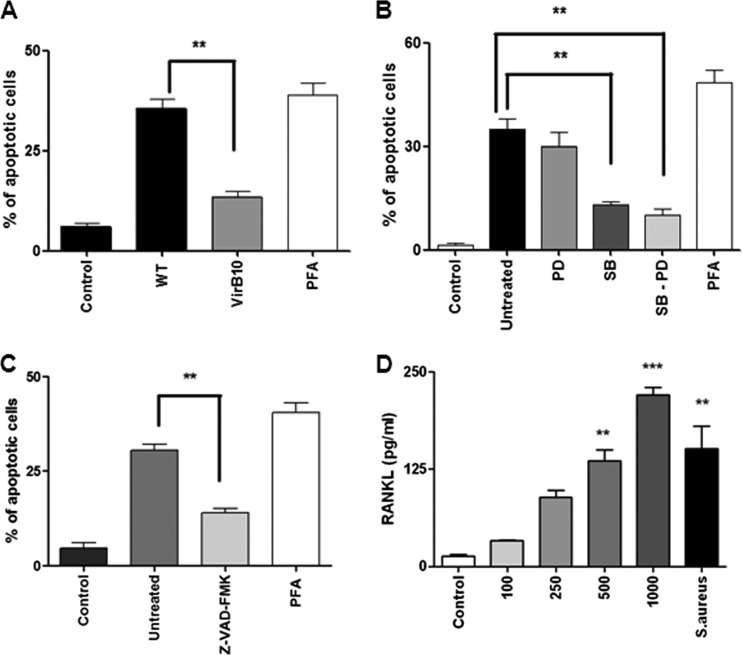
Fig 5.
B. abortus induces RANKL expression on osteoblasts and apoptosis of these cells in a way that is dependent on a functional T4SS, MAPKs, and caspases. (A) Analysis by fluorescence microscopy of apoptotic cells by Hoechst 33342. Primary mouse osteoblasts were infected at an MOI of 100 with either wild-type B. abortus (WT) or its isogenic virB10 mutant (VirB10). **, P < 0.01 versus the results for cells infected with the virB10 mutant. Paraformaldehyde (PFA) was used as a positive control for apoptosis. (B) Primary mouse osteoblasts were infected at an MOI of 100 with B. abortus and treated or not with ERK1/2 inhibitor PD98059 (PD), p38 inhibitor SB23850 (SB), or both inhibitors administered together (PD-SB). **, P < 0.01 versus the results for cells treated with inhibitors. (C) Primary mouse osteoblasts were treated with a general caspase inhibitor, Z-VAD-FMK, and 2 h later, cells were infected with B. abortus. **, P < 0.01 versus the results for cells treated with the general caspase inhibitor. (D) RANKL production by primary mouse osteoblasts infected with B. abortus at different MOIs (100 to 1,000) or not stimulated (Control). Staphylococcus aureus at an MOI of 100 was used as a positive control. P values for comparison with the results for uninfected cells (Control) are as follows: **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. Data shown are from a representative experiment of five performed.