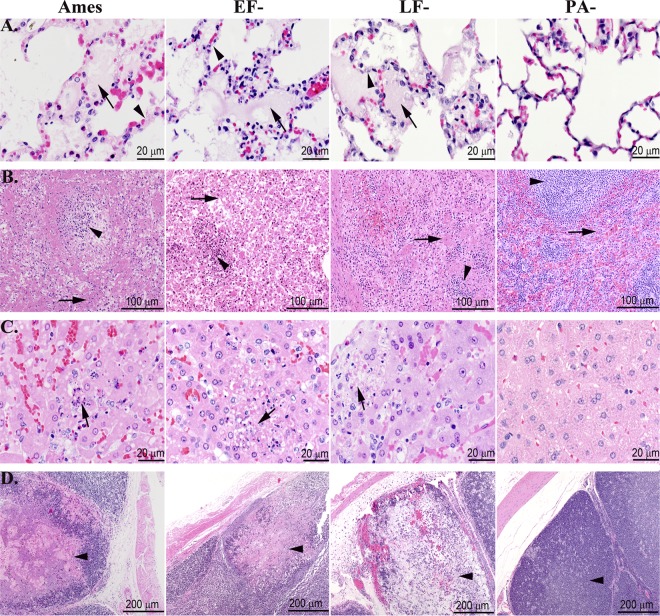
Fig 4.
Terminal microscopic lesions in the lungs, spleens, livers, and cecal appendices were similar for rabbits challenged i.v. with lethal doses of vegetative Ames strain or either of the single toxin deletion mutants. (A) Lungs. The lungs of rabbits succumbing to WT, EF−, and LF− strains had alveolar septal walls (arrowheads) that were distended by fibrin and protein-rich fluid, which frequently exuded into alveoli (arrows). The lungs of rabbits challenged i.v. with the PA− strain were normal. (B) Spleen. The splenic red pulp (arrows) of the rabbits succumbing to WT, EF−, and LF− strains were necrotic, and fibrin was frequently deposited in red pulp sinuses. The splenic white pulp (arrowheads) of the rabbits succumbing to WT, EF−, and LF− strains exhibited necrosis and depletion of lymphocytes. The spleens of rabbits challenged with the PA− strain were normal. (C) Liver. The hepatic sinusoids of rabbits succumbing to WT, EF−, and LF− strains contained necrotic cell debris and heterophils, and there were small foci of hepatic necrosis (arrows) and loss of hepatocytes. The livers of rabbits challenged with the PA− strain were normal. (D) Cecal appendix. The cecal appendices of rabbits succumbing to WT, EF−, and LF− strains exhibited mucosal edema with necrosis and depletion of lymphoid tissue (arrowheads) and replacement by edema, fibrin, and/or hemorrhage. The cecal appendices of the PA− rabbits were normal. Hematoxylin and eosin staining was used.