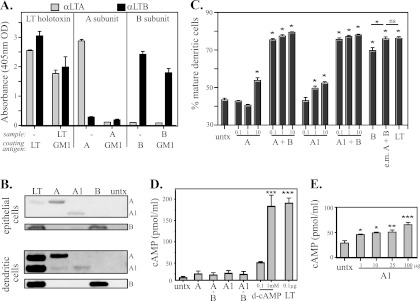
Fig 2.
The A subunit does not bind to GM1 and has altered cellular internalization and ability to induce dendritic cell maturation and cAMP accumulation compared to LT holotoxin. (A) GM1-binding ELISA with LT A and B subunits detected with rabbit anti-LTA or anti-LTB. (B) Western blots of cell lysates of epithelial cells or dendritic cells probed with anti-LTA or anti-LTB rabbit sera 24 h after treatment with A and A1. Both were internalized, but the band intensities differed from that of LT. untx, untreated. (C) Percent mature DCs after 24 h of culture with A or A1 (0.1, 1, or 10 μg) alone or admixed with B subunit (1 μg) or in equal molar (e.m.) ratios equivalent to that in LT holotoxin. Both A and A1 induced dose-dependent maturation of DCs (P < 0.05), which was greatly enhanced with admixed B subunit (B versus any combination of A plus B or A1 plus B, P < 0.05). (D) cAMP levels in epithelial cells after 3 h of incubation with 1 μg A or A1 alone or admixed with 1 μg B subunit compared to d-cAMP or trypsinized LT. (E) cAMP levels in epithelial cells treated with escalating doses (1 to 100 μg) of A1. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ns, not significant compared to untreated cells as calculated by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple-comparison posttest. The error bars indicate standard errors of the means.