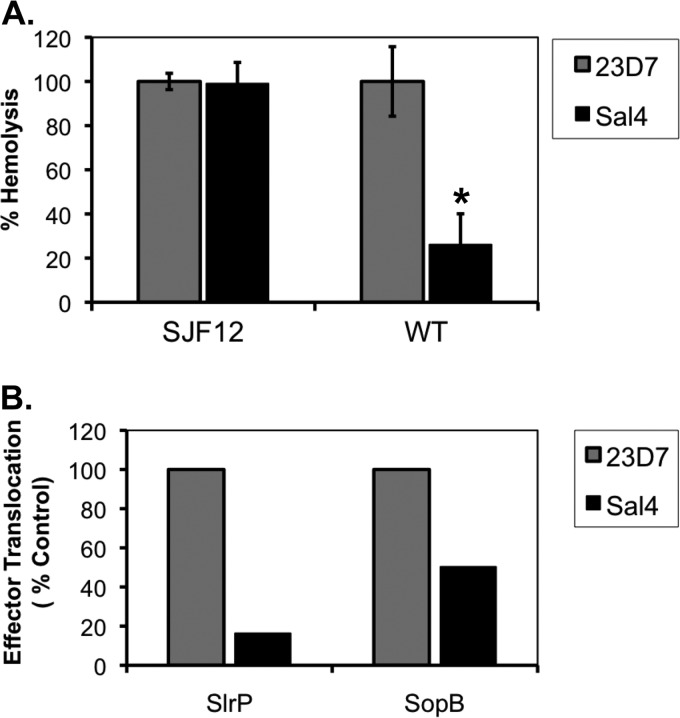
Fig 1.
Reduced activity of the SPI-1 T3SS in the presence of Sal4. (A) Hemolysis as an indirect reporter of SPI-1 T3SS activity. Strains SJF12 and 14028 (WT) were incubated with Sal4 (5 μg/ml) or the ricin toxin-specific isotype control MAb 23D7 (5 μg/ml) for 15 min before the addition to 50% sheep whole blood, as described in Materials and Methods. SJF12 lacks the O5 epitope due to a chromosomal mutation in the oafA gene, which encodes a membrane-integral acetylase (58). The amount of hemolysis associated with each experimental condition was expressed as a percentage of the activity of the wild type or oafA strains alone. The data are the averages (with standard errors [SE]) from a single representative experiment done in triplicate. Sal4 treatment resulted in a statistically significant (*, P < 0.05) reduction in hemolytic activity, as determined by the Student t test. (B) Delivery of SPI-1 T3SS effector proteins into host cells. S. Typhimurium strains JS899 and JS898 expressing the chromosomally encoded effector protein SlrP or SopB, respectively, fused to GSK, were tested in HeLa cell invasion assays in the presence of Sal4 (5 μg/ml) or 23D7 (5 μg/ml), as described in Materials and Methods. Western blots of HeLa cell lysates probed with a GSK-specific antibody were subjected to densitometry. The values plotted on the y axis (“effector translocation”) are relative to the amount of GSK detected in HeLa cells infected with strain 14028 in the absence of either 23D7 or Sal4.