Fig 1.
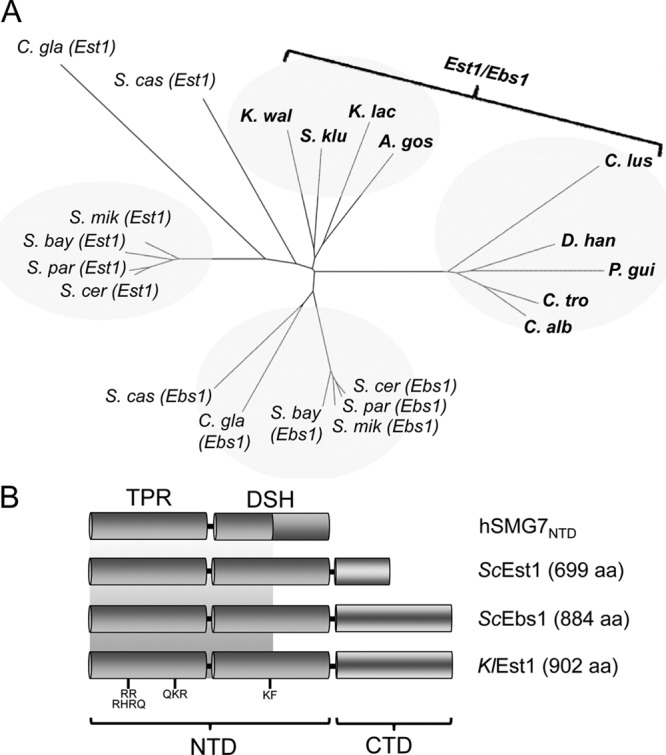
Phylogenetic analysis and domain comparison of Est1/Ebs1 homologues in budding yeast. (A) The relationships between the yeast Est1/Ebs1 homologues were analyzed using the neighbor-joining method and the results were plotted using FigTree. The abbreviations are as follows: A. gos, Ashbya gossypii; C. gla, Candida glabrata; C. alb, Candida albicans; C. lus, Candida lusitaniae; C. tro, Candida tropicalis; D. han, Debaromyces hansenii; K. lac, Kluyveromyces lactis; K. wal, Kluyveromyces waltii; P. gui, Pichia guilliermondii; S. bay, Saccharomyces bayanus; S. cas, Saccharomyces castellii; S. cer, Saccharomyces cerevisiae; S. klu, Saccharomyces kluyveri; S. mik, Saccharomyces mikata; S. par, Saccharomyces paradoxus. (B) The domain structures of the indicated Est1/Ebs1 homologues are depicted. The crystal structure of the N-terminal domain of human SMG7 (hSMG7NDT) revealed a TPR subdomain and a downstream helical subdomain (DSH). The shaded background is used to illustrate the fact that the first half but not the second half of hSMG7DSH aligns well to the yeast homologues.
