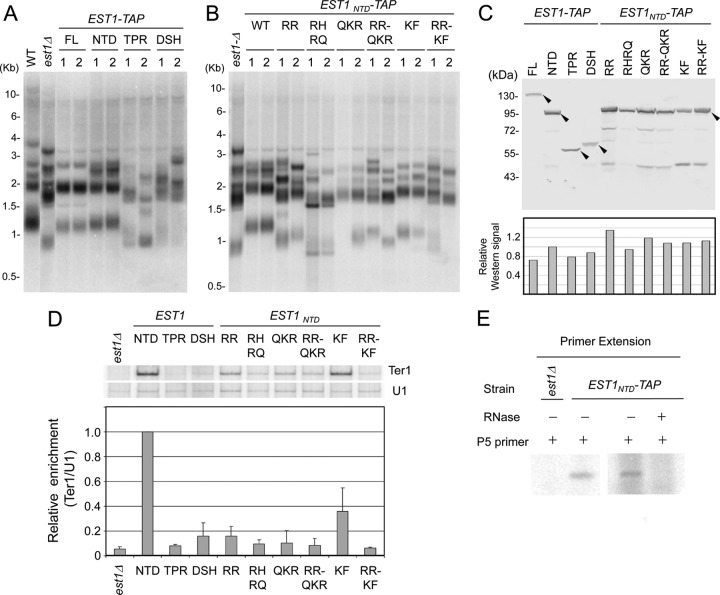
Fig 3.
Effects of EST1 mutations on telomere maintenance and Est1-Ter1 association. (A) Chromosomal DNAs were isolated from the wild-type, est1Δ, and two independently derived strains bearing full-length or truncated EST1 alleles (∼50 generations after the introduction of the EST1 alleles into the null strain) and subjected to Southern analysis of telomere restriction fragments. (B) Same as for panel A, except the chromosomal DNAs were isolated from strains reconstituted with EST1NTD and various point mutants of EST1NTD. (C) (Top) The TAP-tagged Est1 proteins in cell extracts were analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies directed against protein A. (Bottom) Signals were quantified, normalized to that for EST1NTD-TAP, and plotted. (D) (Top) Extracts were prepared from the est1Δ mutant as well as strains reconstituted with various EST1 alleles and subjected to the IgG-Sepharose pulldown assay. The levels of Ter1 and U1 RNA in the pulldown samples were measured by RT-PCR. P32-labeled dCTP was included in the reaction mixtures to allow identification of the PCR products by PhosphorImager scanning of gels. (Bottom) The radioactive signals for the Ter1 and U1 RT-PCR products were quantified by PhosphorImager analysis, and the ratios of Ter1 to U1 products were calculated and plotted. Data are derived from two independent experiments. (E) The IgG-Sepharose pulldown samples from the indicated strains were subjected to primer extension assays using the P5 primer and [α-32P]dGTP.