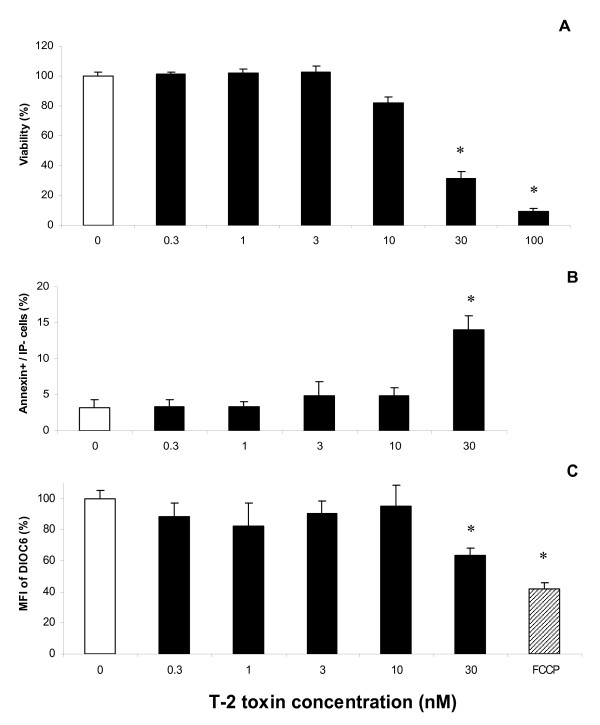
Figure 1.
Cell viability and apoptosis induced by T-2 toxin in porcine alveolar macrophages (PAM). A-Decrease of cell viability in PAM treated with different T-2 toxin concentrations. PAM cultures were exposed to 0.3–100 nM of T-2 toxin for 16 h. Cell viability was assessed by measurement of ATP release. B- Increase of apoptosis in PAM as a function of different T-2 toxin concentrations. PAM cultures were exposed to 0.3 to 30 nM of T-2 toxin. Apoptotic cells were analyzed by flow cytometry using a double staining AnnexinV/IP. C- Decrease of mitochondrial membrane potential (Δψm) in PAM treated with T-2 increasing toxin concentrations. PAM cultures were exposed to 0.3 to 30 nM of T-2 toxin, followed by flow cytometry analysis of DIOC6 probe. A positive control, FCCP (Carbonyl cyanide 4-(trifluoromethoxylphenylhydrazone)) was used to establish a loss of mitochondrial membrane potential (Δψm). All data were reported to the negative control including only the vehicle (0-DMSO), used as 100% of cell viability. Data are shown as mean +/− SEM with PAM from three different piglets are shown and were performed in triplicate. * indicates a P value < 0.05.