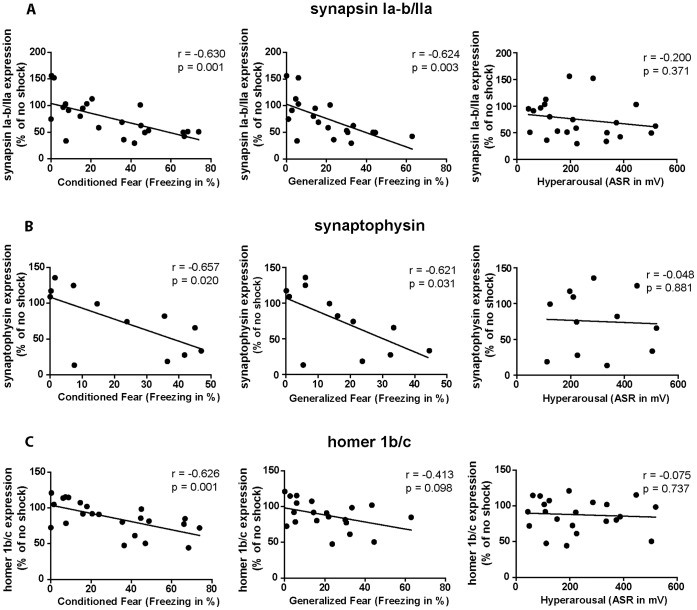
Figure 5. Hippocampal SV protein expression correlates negatively with the generalized and the conditioned fear response but not with hyperarousal.
(A–C) Statistical correlation of protein expression levels with behavioral data in shocked and non-shocked mice: intensities of the different symptoms of the murine PTSD-like syndrome, i.e. conditioned fear, generalized and the acoustic startle response (ASR), were plotted against the relative day-60 protein expression levels (% of no shock) of synapsin Ia–b/IIa (A), synaptophysin (B) and homer 1b/c (C) of both shocked and control mice (i.e. each cloud of dots comprises both shocked and mock-treated mice). Pearson correlation coefficients (“r”) were calculated and a two-tailed student’s t-test was performed (“p”), n = 12 (batch PTSD I and II) for synapsin Ia–b/IIa and homer 1b/c, n = 6 (batch PTSD I only) for synaptophysin (synapsin: conditioned fear: r = −0.630, p = 0.001; generalized fear: r = −0.624, p = 0.003; hyperarousal: r = −0.200, p = 0.371; synaptophysin: conditioned fear: r = 0.657, p = 0.020; generalized fear: r = −0.621, p = 0.031; hyperarousal: r = −0.048, p = 0.881; homer 1b/c: conditioned fear: r = −0.626, p = 0.001; generalized fear: r = −0.413, p = 0.098; hyperarousal: r = −0.075, p = 0.737).