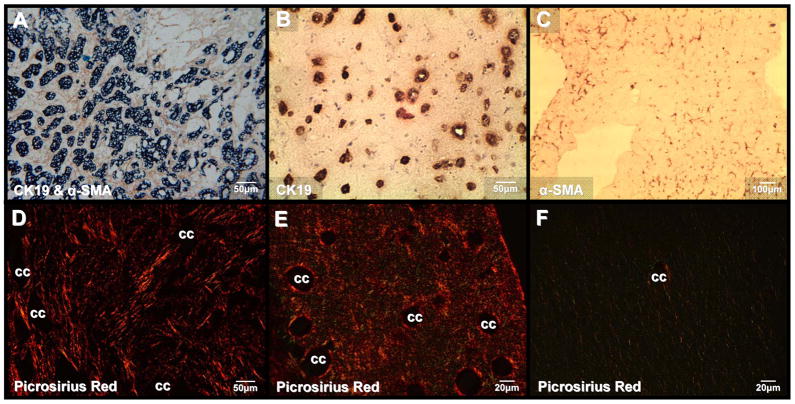
Figure 3.
Co-culturing of BDEsp-TDEH10 cells with BDEsp-TDFE4 cells in rat tail type I collagen gel matrix reproduces characteristic histopathological features of desmoplastic BDEsp ICC in vivo. (A) Desmoplastic BDEsp ICC formed in rat liver showing selective positive immunostaining of well differentiated cholangiocarcinoma ducts for biliary cytokeratin 19 (CK19) (blue staining) and cancer-associated myofibroblastic cells positive for α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) (brown staining) in the surrounding tumor stroma. (B) Like BDEsp ICC, well differentiated “duct-like” structures formed from BDEsp-TDEH10 cells in organotypic co-culture exhibit selective immunoreactivity for CK19 (brown staining). (C) Also like BDEsp ICC, stromal BDEsp-TDFE4 cells in organotypic co-culture are selectively immunoreactive for α-SMA (brown staining). (D) Picrosirius red staining under polarized light of type I collagenous fibers (orange-yellow) densely populating the desmoplastic stroma of a BDEsp ICC. (E) Picrosirius red staining of a representative histological section of a BDEsp-TDE/BDEsp-TDF co-culture mimicking the strong extracellular staining reaction for type I collagen exhibited by the orthotopic ICC in D. (F) Picrosirius red staining of a BDEsp-TDEH10 control culture without BDEsp-TDF showing only background staining for type I collagen fibers in gel matrix. cc denotes representative cholangiocarcinoma ducts or “duct-like” structures.