Figure 3. Cathepsin H removes NH2-terminal Lys and Arg from Lys-Arg-(Met)enkephalin (KR-ME).
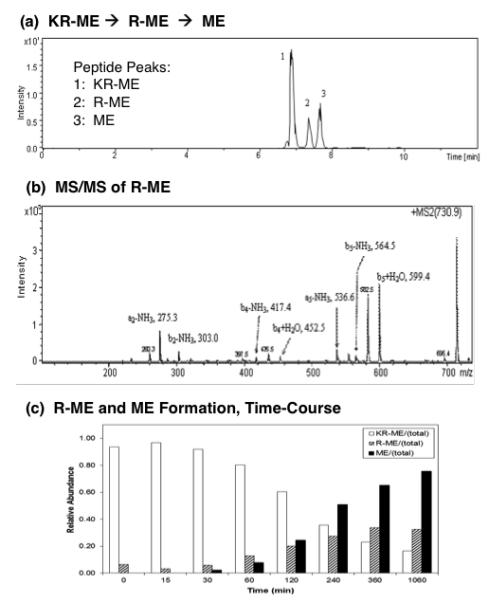
(a) KR-ME substrate conversion to R-ME and M: total ion chromatogram. Cathepsin H was incubated with KR-ME and nano-LC-MS/MS was conducted to identify peptide cleavage products. The total ion chromatogram (TIC) shows the presence of KR-ME substrate, and the products R-ME and ME, based on their masses (shown in supplemental Table 1).
(b) R-ME identified by tandem mass spectrometry. R-ME peptide (RYGGFM) was identified by MS/MS tandem mass spectrometry. The MS/MS spectra is illustrated here; those for KR-ME and ME are shown in supplemental Figure A.
(c) Time-course of cathepsin H production of R-ME and ME from KR-ME. The time course of cathepsin H conversion of KR-ME to R-ME and ME is illustrated by the open bars, hatched bars, and black solid bars, respectively. Using (Met)enkephalin standard peptide, LC peptide peak integrations vary by less than 1%, which we have previously demonstrated (Hwang et al., 2007).
