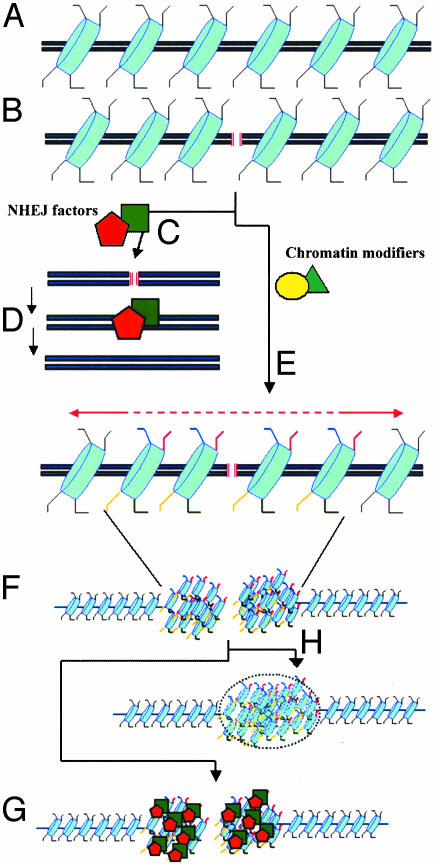
Fig. 1.
Histone modifications during NHEJ. (A) Intact DNA molecule showing the nucleosomes (in blue) and the protruding histone tails (black lines). (B) Generation of a DSB (red lines). During the repair process, at least two types of factors are recruited to the DSB: catalytic factors that heal the lesion by NHEJ (C and D) and enzymes that remodel chromatin by posttranslational changes of residues within the histone tail (e.g., red, phosphorylation; blue, acetylation; yellow, deacetylation) (E). The new pattern of epigenetic marks may trigger the compaction of chromatin in the microenvironment surrounding the break (F). This chromatin reconfiguration would serve to increase the local concentration of NHEJ-catalytic factors (G) and/or limit the diffusion of the broken DNA ends until the break is repaired (H).