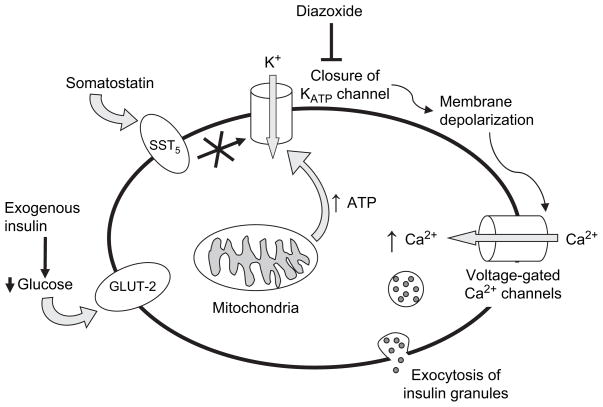
Fig. 1.
Schematic presentation of glucose-mediated insulin secretion and medications that block insulin secretion. Glucose transporter 2 actively transports glucose into β-cells. Lower extracellular glucose concentrations induced by exogenous insulin lead to less glucose uptake. Glucose metabolism induces adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production, causing closure of the ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channels. The altered membrane potential leads to depolarization and influx of calcium via voltage-gated calcium channels. Closure of KATP channels can be directly blocked by KATP channel openers, such as diazoxide, or indirectly blocked by second-messenger systems triggered by interaction of somatostatin with the sst5 receptor. Somatostatin may also have direct effects on calcium channels.