Figure 4.
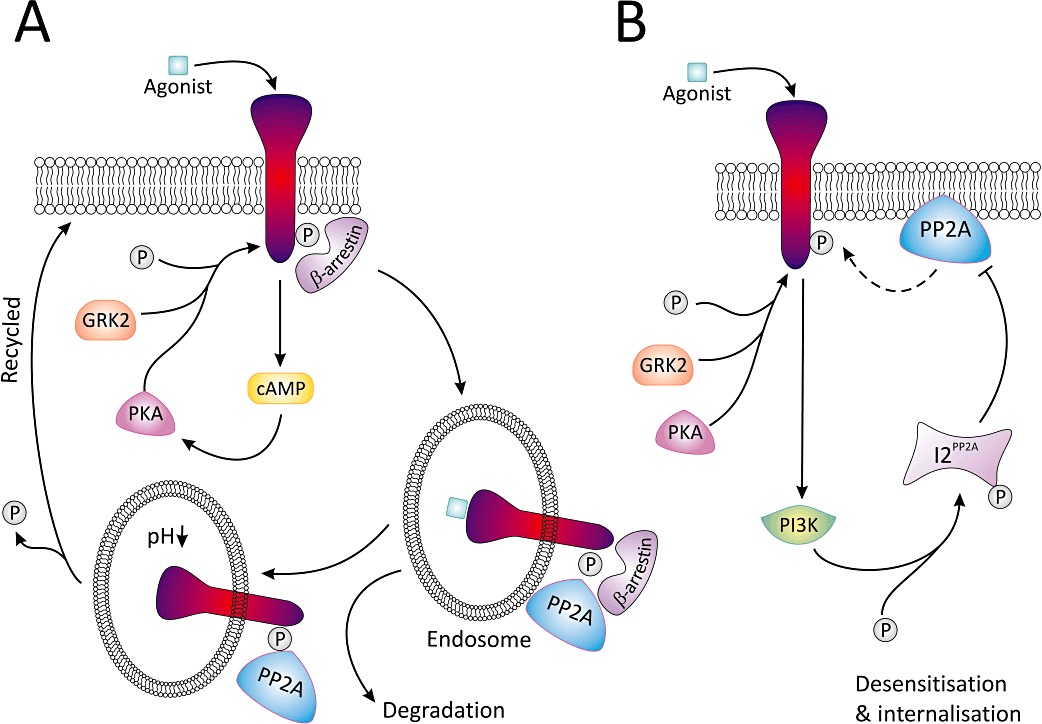
A summary of the role PP2A and its inhibitor I2PP2A have in β-adrenoceptor resensitization (A) and desensitization (B). (A) Following agonist, cAMP levels are elevated and either PKA or GRK2 phosphorylate the receptor permitting binding of β-arrestin. The receptor β-arrestin complex undergoes sequestration into the endosome; following acidification, β-arrestin is released and PP2A dephosphorylates the receptor. As a result of this, the receptor is resensitized and may be recycled back to the plasma membrane. (B) Alternatively, agonist binding and receptor phosphorylation can lead to PI3K activation, which phosphorylates I2PP2A thereby inhibiting PP2A-mediated dephosphorylation of the receptor at the plasma membrane, thus driving the system towards desensitization and internalization of the receptor.
