Figure 1.
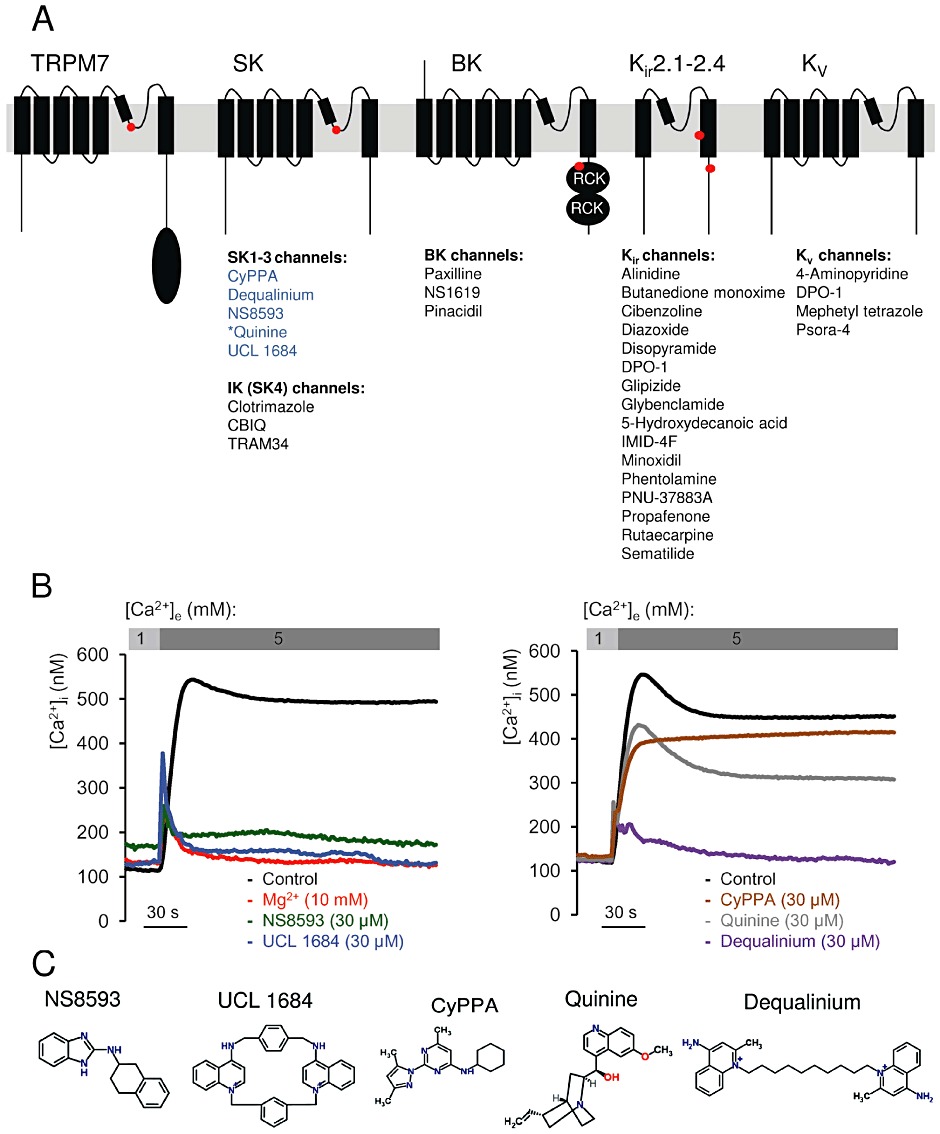
Identification of TRPM7 channel inhibitors among known modulators of Mg2+ sensitive K+ channels. (A) Domain architecture of TRPM7, KCa2.1–2.3 (SK), KCa3.1 (IK, SK4), KCa1.1 (BK), KIR and KV channels. Locations of Mg2+-binding sites in TRPM7 (formed by E1047 and Y1049 in mouse TRPM7 (Mederos y Schnitzler et al., 2008), KCa2.1–2.3 channels [S359 in rat KCa2.2 (Soh and Park, 2002)], KCa1.1 channels (formed by E374 and E399 in human BK1) (Wu et al. 2010; Yang et al., 2008), KIR channels (D172 and E224 in mouse KIR2.1) (Stanfield et al., 1994; Wible et al., 1994; Taglialatela et al., 1995) are indicated by red dots. KD, Ser/Thr kinase domain in TRPM7; RCK, ‘regulating the conductance of K+’ domain in KCa1.1 channels. The modulators of K+ channels tested in a primary screen for TRPM7 inhibitors are listed below their known targets. Compounds labelled in blue were found to be inhibitors of TRPM7, while modulators in black showed no inhibitory effect on TRPM7. *Quinine blocks KCa1.1 and KCa3.1 channels. (B) Primary assessment of modulators using a bioluminescence-based assay of TRPM7 channel activity. Representative traces are shown from two independent experiments with similar results. The indicated compounds (30 µM) or Mg2+ (10 mM) were applied to ponasterone A-induced HEK 293 cells, and the measurements were performed in the presence of 1 or 5 mM external Ca2+ ([Ca2+]e) as indicated. (C) Chemical structures of TRPM7 inhibitors identified.
